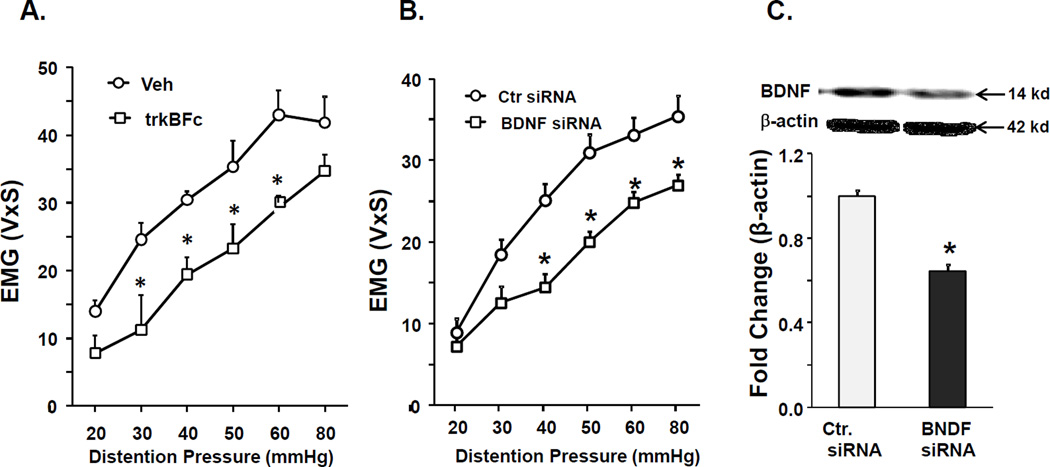
Figure 3.
Intrathecal treatment with BDNF antagonists reduced VMR to CRD in female CPS+HeICS rats. A. Graph shows that intrathecal administration of BDNF antagonist trkBFc in female CPS rats significantly decreased VMR to CRD, 24 hours following adult 2× HeICS (2 way repeated measures ANOVA found a significant main effect of treatment, F1,53=10.4, p=0.015; post hoc tests found significant differences at 30 mmHg, 40 mmHg, 50 mmHg and 60 mmHg, n=4). B. Graph shows that intrathecal administration of BDNF siRNA in female CPS rats significantly decreased VMR to CRD, 24 hours following adult 2× HeICS (2 way repeated measures ANOVA: treatment×pressure interaction, F1,77=3.49, p=0.008, tukey post hoc tests found significance at 30 mmHg, p=0.013 and at 40, 50 50, 80 mmHg, p<0.001, n=7 Ctr., n=6 BDNF siRNA). C. Western blot shows a significant decrease in spinal cord BDNF protein expression in rats treated with BDNF siRNA (*p<0.05).