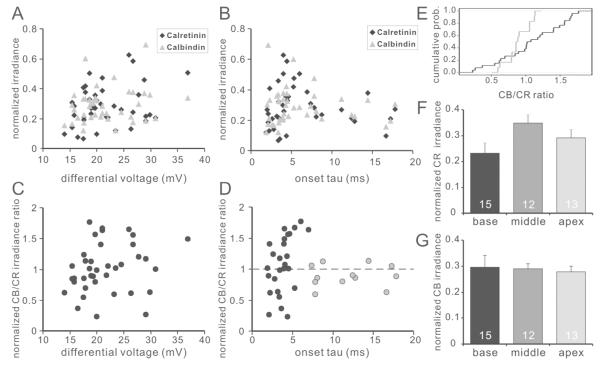
Figure 8. Normalized calbindin/calretinin staining irradiance ratio correlates with action potential kinetics.
A-B, relation of calretinin (black diamond) and calbindin (gray triangle) staining irradiance with differential voltage (A) and threshold onset time course (B). Each data point represents a single recording from one neuron. Neither calretinin nor calbindin staining irradiance correlate with the tested neuronal intrinsic firing properties. C-D, Relationship between the ratio of normalized calbindin to calretinin staining irradiance with differential voltage (C) and onset tau (D). Data from neurons with fast (onset tau< 7.0ms) and slow (onset tau>7.0ms) kinetics were color coded in black and gray, respectively. E, Cumulative probability of the normalized calbindin/calretinin staining irradiance of fast (black curve) and slow (gray curve) neurons shown in D; two sample Kolomgorov-Smirnov test, p<0.05. F-G, average calretinin (F) and calbindin (G) staining irradiance of recorded neurons from different tonotopic regions show a similar trend as in Fig. 4 and Fig. 5.