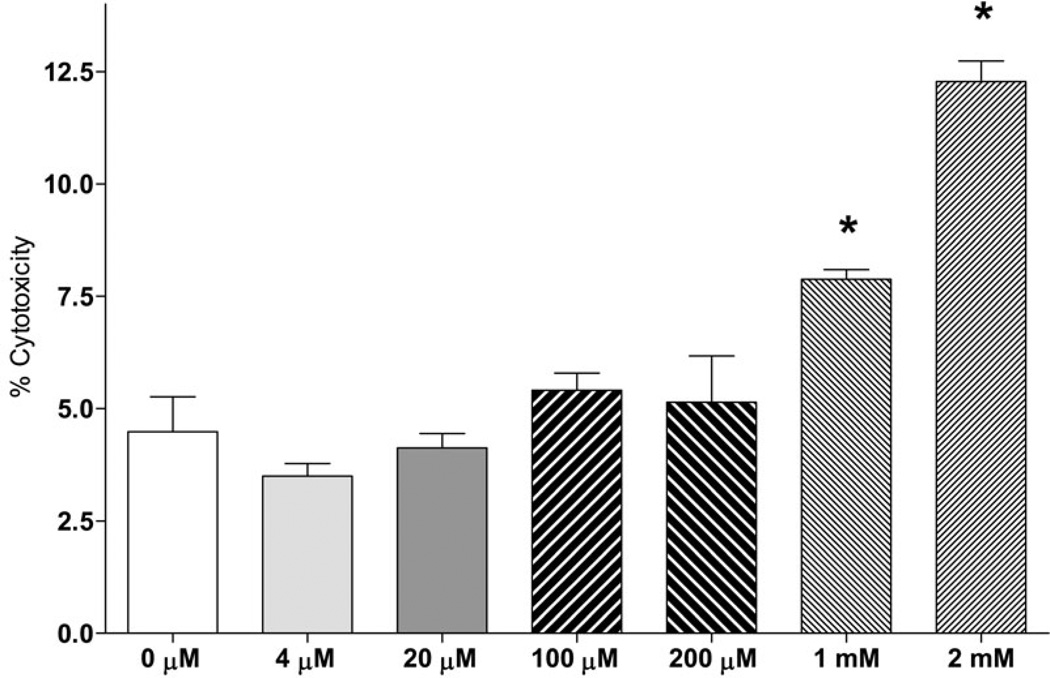
Fig. 2. Incorporation of radiolabeled substrates into total lipids and total fatty acids in a neuronal cell line.
Incorporation of radiolabeled substrates into total lipids (A) and total (free + esterified) fatty acids (B) upon incubation of SH-SY5Y cells with 2 µCi of [U-14C]glucose (Glc), [U-14C]aspartate (Asp), [U-14C]glutamine without non-labeled glutamate (Gln), [U-14C]glutamine with 3.8 µM non-labeled glutamate (Gln+Glu), or [U-14C]glutamate (Glu) for 18h under 19% O2 (normoxia) and 1% O2 (hypoxia). Cells were preconditioned in serum-free medium for 24 h under normal or hypoxic condition, and for another 18 h with radiolabeled tracer. At the end of incubation, lipids were extracted from cells using chloroform/methanol by the Folch protocol. An aliquot of the extract was analyzed for total lipid radioactivity (A). Another aliquot of the lipid extracts was saponified with KOH and separated by TLC for total fatty acid radioactivity analysis (B). Insets represent Glc, Asp, Gln, and Gln + Glu incorporation at a smaller scale. Addition of non-labeled aspartate (0.5 mM) did not affect the 14C incorporation rates from all substrates. * - significantly different as compared to 19% O2. Values are mean ± SD, n=3.