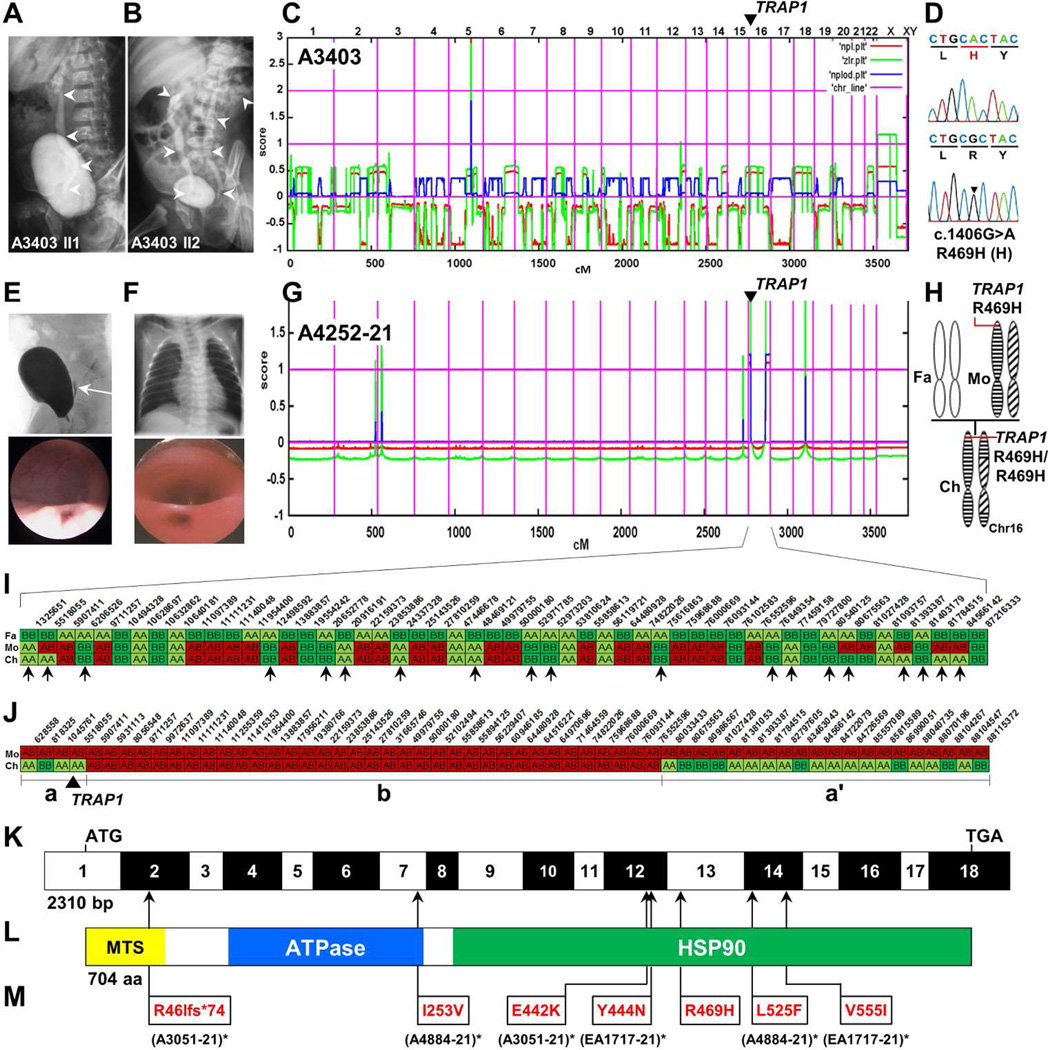
Figure 1. Homozygosity mapping and whole exome resequencing identifies mutations in TRAP1 as causing CAKUT or VACTERL association.
(A, B) Voiding cysturethrograms (VCUG) of CAKUT siblings A3403-21 and -22 showing unilateral vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) grade III and bilateral VUR, respectively (white arrow heads).
(C) Non-parametric LOD (NPL) scores across the human genome in 2 affected sibs. X-axis represents Affymetrix 250k StyI array SNP positions across human chromosomes concatenated from p-terminal (left) to q-terminal (right). Genetic distance is given in cM. A single peak indicates distantly related parents.
(D) Chromatogram of newly identified homozygous missense mutation (arrow head) in the gene encoding TNF receptor-associated protein 1 (TRAP1) over wild type control.
(E) VCUG (upper panel) and cystoscopy (lower panel) demonstrating VUR and a dilated ureteral orifice, respectively.
(F) Chest X-ray (top panel) and esophagoscopy (bottom panel) showing esophageal atresia and esophagotracheal fistula in individual A4252-21 with CAKUT in VACTERL association.
(G) NPL score in an individual A4252-21 with VACTERL association. Two maximum peaks indicate homozygosity at the p-terminus and q-terminus of chromosome 16.
(H) Panel on the right illustrates maternal heterodisomy of chromosome 16 and partial uniparental isodisomy (p-ter and q-ter) of the child (Fa, father; Mo, mother; Ch, child).
(I) Partial haplotypes of selected markers and their physical positions across chromosome 16 in the father (Fa), the mother (Mo), and the affected child (Ch) of CAKUT family A4252. Selected markers (biallelic SNPs; MAF = 0.496 – 0.5) homozygous in the father are shown in green (alleles AA) and light green (alleles BB).
The fact that for 19 of 52 alleles there is paternal non-contribution in the child strongly suggests maternal heterodisomy of chromosome 16. No paternal non-contribution was observed in the child on any other chromosome (data not shown).
(J) Selected markers (biallelic SNPs; MAF = 0.497 – 0.5) heterozygous in the mother (Mo) of family A4252 are shown for alleles coded in red (AB; phase unknown). Note that in the central segment (b), separated by vertical lines, the child’s (Ch) haplotype is identical to the mother’s. In the p-ter (a) and q-ter (a’) segments (a, a’) the child is homozygous, indicating maternal isodisomy in these segments.
(K) Exon structure of human TRAP1 cDNA. Positions of start codon (ATG) and of stop codon (TGA) are indicated.
(L) Domain structure of the TRAP1 protein. HSP, heat shock protein; MTS, mitochondrial targeting sequence.
(M) Translational changes of detected mutations are shown relative to their positions in TRAP1 cDNA (see L) and TRAP1 protein (see M) for affected individuals with CAKUT or CAKUT in VACTERL association with recessive TRAP1 mutations. Family numbers are shown in parenthesis. (* denotes an individual carrying a compound hete)