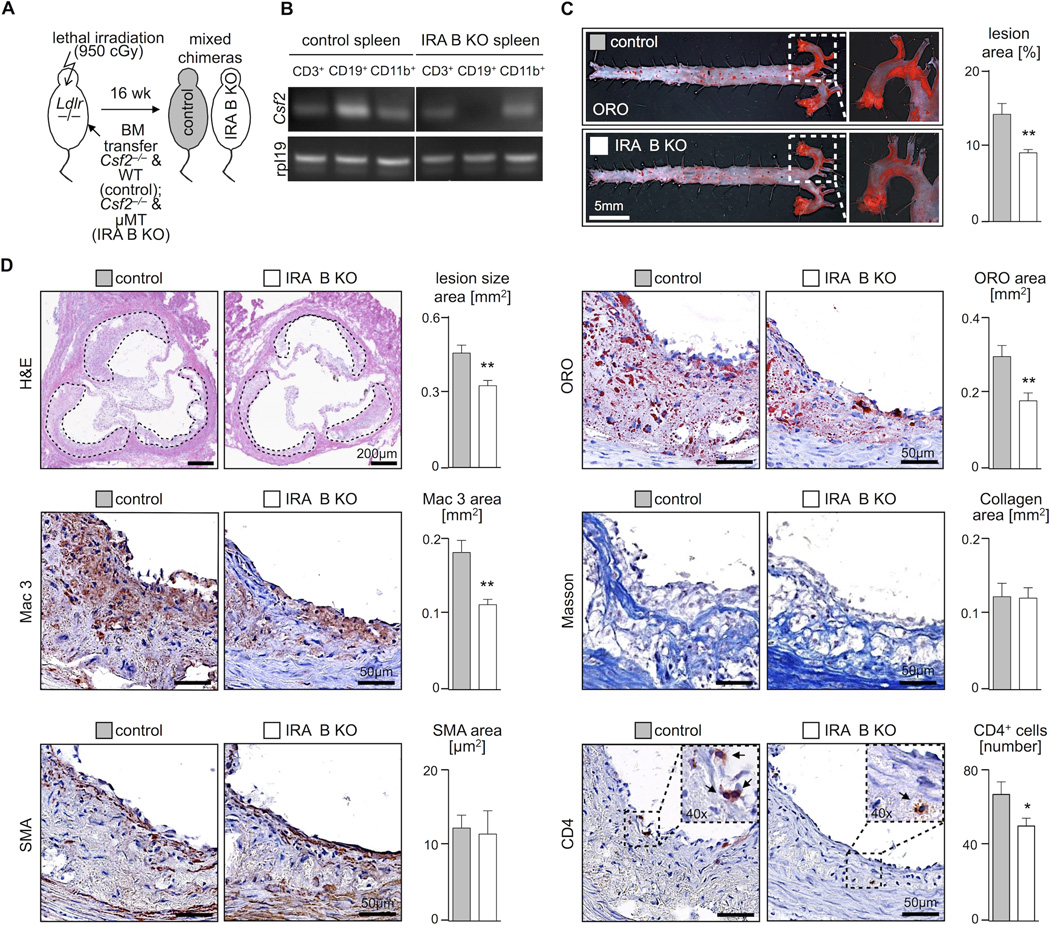
Figure 2.
IRA B cells promote atherosclerosis. (A) For generation of mixed bone marrow chimeras with B cell restricted GM-CSF deficiency (IRA B KO) lethally irradiated 8 week old Ldlr−/− mice were reconstituted with a 50:50 mixture of GM-CSF deficient (Csf2−/−) and B cell deficient (µMT) bone marrow (white). Control mice were reconstituted with a 50:50 mixture of GM-CSF deficient (Csf2−/−) and WT bone marrow (gray). After 6 weeks of reconstitution mice were placed on HCD for another 10 weeks. (B) Validation of B cell restricted GM-CSF deficiency in IRA B KO mice after reconstitution and 10 weeks of HCD. Identification of GM-CSF (Csf2) mRNA expression by semi-quantitative reverse transcription PCR in sorted CD3+ (T cells), CD19+ (B cells) and CD11b+ (myeloid cells) splenocytes from control and IRA B KO mice. Rpl19 serves as the housekeeping gene. (C) En face Oil-Red-O (ORO) staining of excised aortas from control and IRA B KO mice after 10 weeks of HCD on the left and quantification of lesion area on the right (n = 7 per group). Results are presented as means ± SEM, ** p ≤ 0.01, gray color for control, white color for IRA B KO mice. (D) Representative H&E staining of aortic root sections from control (gray) and IRA B KO (white) mice after 10 weeks of HCD with quantification of lesion size in two independent experiments (n ≥ 20 per group). Results are presented as means ± SEM. In addition immunohistology depicting ORO-, Mac3-, smooth muscle actin (SMA)-, Masson’s trichrome (Masson) and CD4-positive staining of aortic root lesions representative of both groups with quantification of n ≥ 10 samples per group. Results are presented as mean ± SEM, * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01.