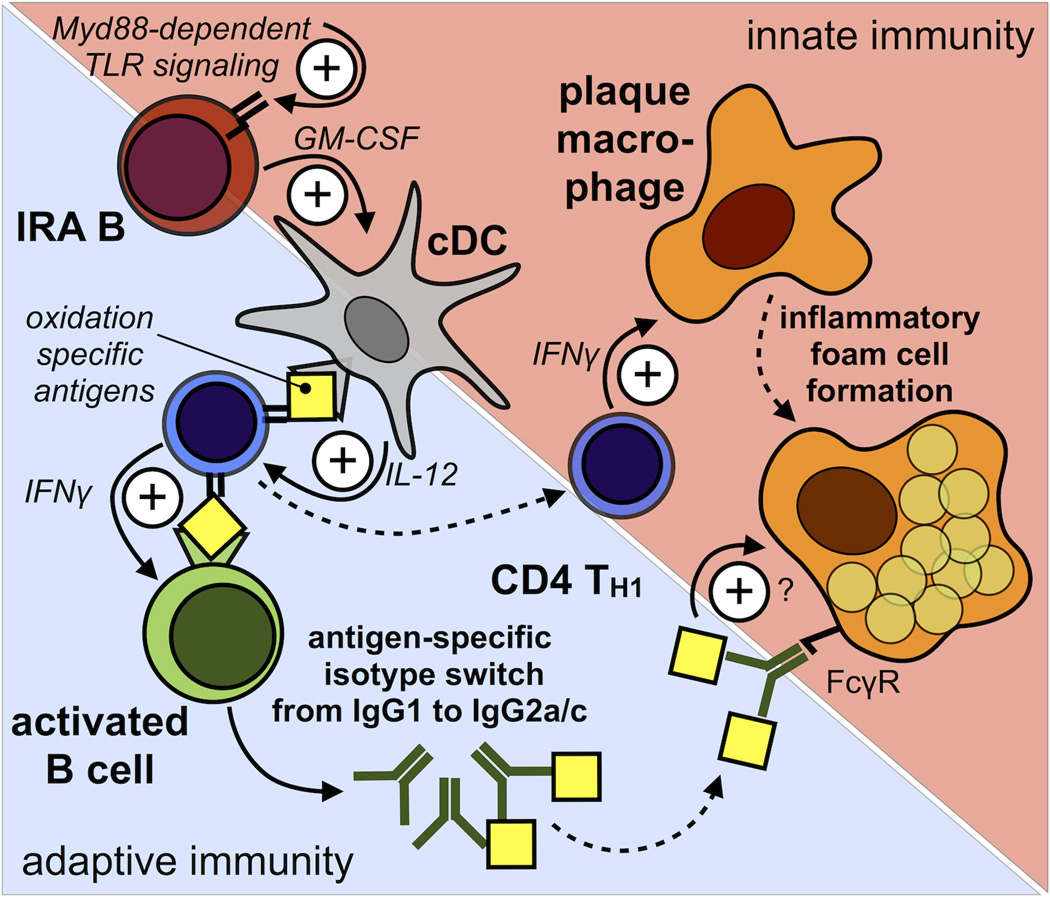
Figure 6.
Model of IRA B cell-dependent TH1 skewing during atherosclerosis. During atherosclerosis IRA B cells arise in secondary lymphoid organs via Myd88-dependent signaling and promote the generation of classical IL-12 producing classical dendritic cells (cDC). CD4+ T-helper cells that recognize disease related antigens (i.e. oxidation specific epiptopes) presented by these cDC differentiate into IFNγ-producing TH1 cells. TH1 cells infiltrate atherosclerotic lesions and stimulate macrophages. Antigen-specific interaction between TH1 cells and B cells leads to IFNγ-dependent isotype switching from IgG1 to IgG2a/c which carry the highest Fcγ-receptor mediated activation capacity. By instructing TH1-priming cDC IRA B cells aid in bridging innate and adaptive immunity. Solid arrows depict functional relationship and dashed arrows depict spatial relationship.