Table 1.
Anodic coupling of amines and dithioketene acetals.
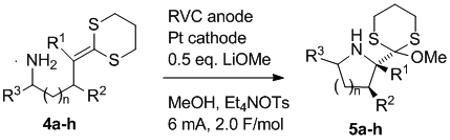
| Entry | Subst. | n | R1,R2,R3 |
Ep/2[a] [V] |
Yield[b] [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4a | 1 | R1 = Me R2 = R3 = H |
0.60 | 84 |
| 2 | 4b | 1 | R1 = R2 = Me R3 = H |
0.62 | 81 (>20:1) |
| 3 | 4c | 1 | R1 = R3 = Me R2 = H |
0.58 | 92[c] (3:2) |
| 4 | 4d | 1 | R1 = CH=CHMe R2 = Me, R3 = H |
-- | 90 (10:1) |
| 5 | 4e | 2 | R1 = Me R2 = R3 = H |
0.65 | 72 |
| 6 | 4f | 2 | R1 = R2 = Me R3 = H |
0.68 | 83[d] (10:1) |
| 7 | 4g | 2 | R1 = R3 = Me R2 = H |
0.67 | 64[e] (2:1) |
| 8 | 4h | 3 | R1 = Me R2 = R3 = H |
0.70 | -- |
Measured vs. Ag/AgCl on a carbon anode in acetonitrile.
Ratio in parenthesis is diastereomeric ratio.
A 40% yield (measured by 1H NMR using an internal standard) of product was obtained when 6 eq. of 2,6-lutidine was used as the base instead of LiOMe.
2.3 F/mol.
2.4 F/mol.
