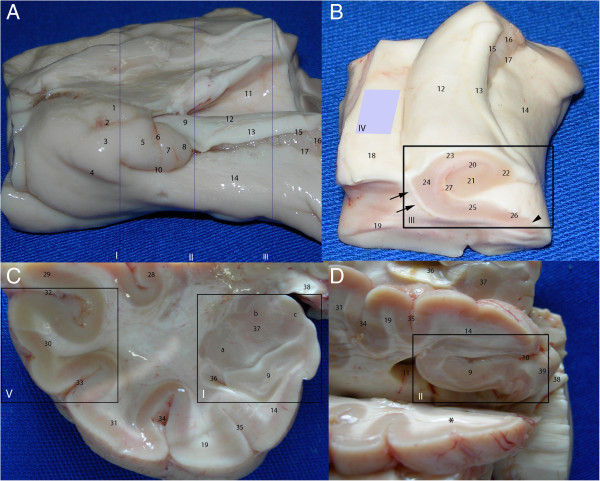
Figure 1.
Temporal lobe dissection for the study of neurogenic niches. The panels show the following different angles of the temporal lobe: medial (A); anteromedial, from the body of the hippocampus (B); coronal cut at the level of the amygdala (C); inferomedial, with the head of the hippocampus exposed (D). The following five standard cuts were made: at the levels of the amygdala (A-I and C-I), head of the hippocampus (A-II and D-II), body of the hippocampus (A-III and B-III), ventricular wall containing the SVZ (B-IV) and lateral cortex (C-V). 1, semilunar gyrus, the section of the uncus corresponding to the medial surface of the amygdala; 2, semiannular sulcus; 3, ambient gyrus; 4, tentorial groove; 5, uncinate gyrus; 6, anterior hippocampal sulcus; 7, band of Giacomini; 8, intralimbic gyrus; 9, head of the hippocampus; 10, uncal sulcus (uncal notch); 11, temporal horn of the lateral ventricle; 12, body of the hippocampus; 13, fimbria; 14, parahippocampal gyrus; 15, fimbriodentate sulcus; 16, dentate gyrus (margo denticulatus); 17, hippocampal sulcus; 18, collateral eminence; 19, fusiform gyrus; 20, granule cell layer of the dentate gyrus; 21, cornu ammonis (CA) 4; 22, CA3; 23, CA2; 24, CA1; 25, subiculum; 26, presubiculum; 27, hippocampal fissure; 28, insula; 29, superior temporal gyrus; 30, middle temporal gyrus; 31, inferior temporal gyrus; 32, superior temporal sulcus; 33, inferior temporal sulcus; 34, occipitotemporal sulcus; 35, collateral sulcus; 36, uncal recess; 37, amygdala; 38, optic tract; 39, posteromedial surface of the uncus (including the uncinate gyrus, the intralimbic gyrus and the band of Giacomini). Groups of nuclei of the amygdala: a, basolateral; b, central; and c, corticomedial. The asterisk indicates the slice cut used to obtain the block containing the head of the hippocampus. Arrows: intraparenchymal ependymal layer (see text); arrowhead: medial boundary of DCX expression in the subicular complex.