Figure 31.
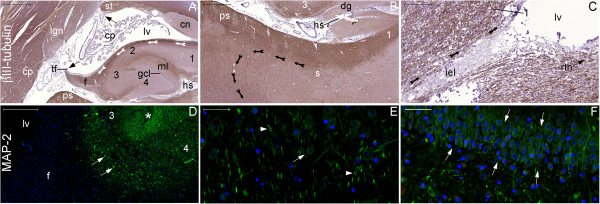
Minor expression of neurogenesis markers in the granule cells of the dentate gyrus. This panel shows coronal sections throughout the body of the hippocampus at different magnifications. Upper and lower lines show βIII-tubulin and MAP-2 staining, respectively. Granule cells of the dentate gyrus (see granule cell layer (gcl) in (A) and between arrows in (F)) and their mossy fibers projecting to CA3 (3) show minor βIII-tubulin (A) and major MAP-2 staining (see the zone surrounding asterisk in (D)). On the other hand, the fimbria (f) shows major βIII-tubulin (A) and no MAP-2 expression (D). Because βIII-tubulin expression is scattered throughout structures such as the cerebral peduncle (cp), it is likely that βIII-tubulin detects immature and mature neurons; in contrast, MAP-2 is a specific marker for mature neurons. Thus, the analysis of this panel indicates that mature neurons mostly form the connections from the granule cells of the dentate gyrus to the hippocampus proper, whereas the efferent pathway of the hippocampal formation (depicted by arrows in (B), (C) and (A)) may contain immature neurons. (1), CA1; (2), CA2; (4), CA4; (cn) tail of the caudate nucleus; (cp), choroid plexus; (dg), margo denticulatum of the dentate gyrus; (hs), hippocampal sulcus; (iel), intraparenchymal ependymal layer; (lgn), lateral geniculate nucleus; (lv), temporal horn lateral ventricle; (ml), molecular layers; (ps), presubiculum; (rth), roof of the temporal horn (arrow points to its direction); (s), subiculum; (st), stria terminalis; (tf), taenia fimbriae. Black arrows in (A): locations of attachment of the choroid plexus to the brain. White arrows in (D) and (E): pyramidal cells; white arrowheads: MAP-2 positive fibers. Scale bars: (A) = 2,000 μm; (B) = 1,000 μm; (C) = 100 μm; (D) = 500 μm; (E), (F) = 50 μm.
