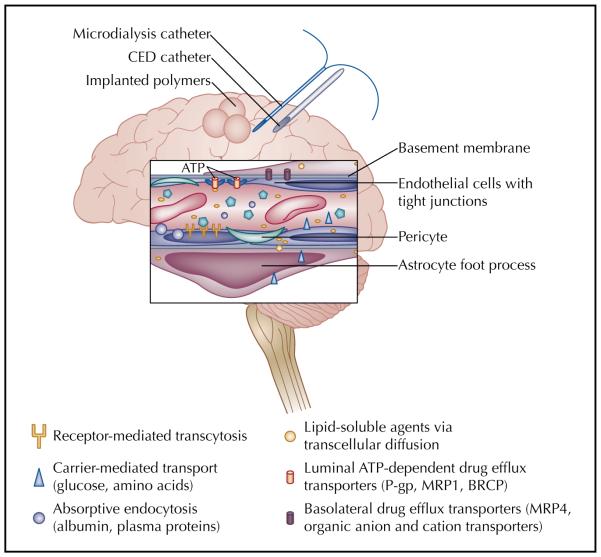
Figure 1.
Schematic of the components of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), includ ing endothelial cells with tight junctions, pericytes, basement membrane, drug efflux transporters, and astrocytic foot processes. Various mechanisms for transport across the BBB, including transcellular diffusion, absorptive endocytosis, carrier-mediated transport, and receptor-mediated transcytosis, are also represented. Finally, approaches to deliver drugs directly to the brain and to assess drug concentration within brain tissue are displayed. ATP—adenosine triphosphate; BCRP—breast cancer resistance protein; CED—convection-enhanced delivery; MRP—multidrug resistance protein; P-gp—P glycoprotein.