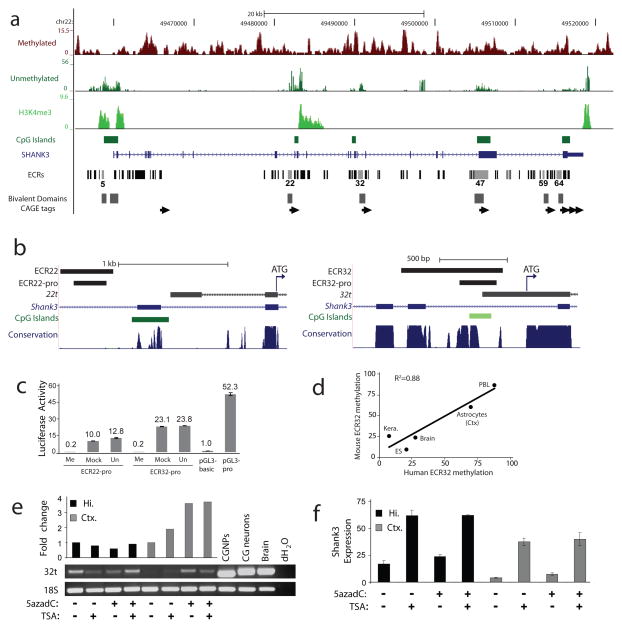
Figure 3. Novel transcripts initiate from differentially methylated, evolutionarily conserved intragenic promoters in a cell context-dependent manner.
a, Human frontal cortex MRE-seq, MeDIP-seq and H3K4me3 ChIP-seq at SHANK3 (top). Evolutionarily conserved regions (ECRs) overlap with mouse CAGE tag clusters (arrows), mouse ES H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 bivalent domains27 and human frontal cortex H3K4me3. ECRs with most or all promoter-associated features are shown with light grey bars. b, Diagram of ECR22 (left) and ECR32 (right) mouse genomic regions displaying from top to bottom ECRs, sequences used for promoter assays, 5′ RACE sequences of 22t and 32t with associated ATGs (arrow), known exons, CpG island (dark green) and CpG-rich (light green) regions, and multi-species DNA sequence conservation. c, In vitro methylation of the mouse SHANK3 intragenic promoters abolished their activity in promoter assays. Me, methylated; Mock, mock treated; Un, untreated. d, Bisulfite sequencing of ECR32 in matched tissues/cells from human and mouse. P=0.018; ANOVA regression analysis. e, Increased 32t transcription in cortical, but not hippocampal astrocytes after treatment with 5azadC by transcript-specific RT-PCR (p<0.05, Student’s t-test). Positive controls: untreated primary cultures of cerebellar granule neural progenitor cells (CGNPs), their in vitro differentiated neurons (CG neurons), and whole brain. The 24-bp size difference in CGNPs and CG neurons is due to alternative splicing within the 32t transcript. Hi., hippocampal; Ctx., cortical. f, Increased expression of full-length SHANK3 detected by qRT-PCR in astrocytes treated with TSA alone or in combination with 5azadC (p<0.05, Student’s t-test) but not 5azadC alone.