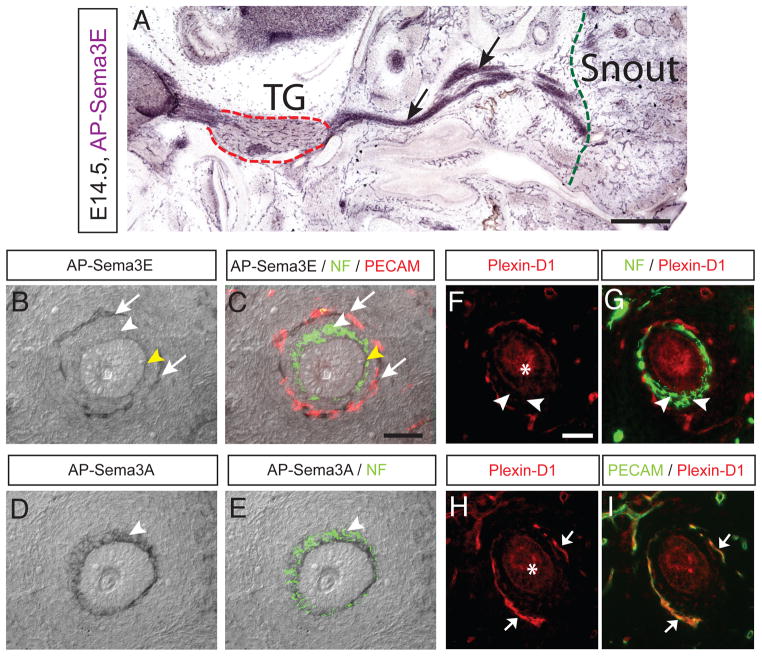
Figure 5. Plexin-D1 protein expression is selectively down-regulated in the target terminal of TG axons.
(A–C) Plexin-D1 protein expression is visualized by AP-Sema3E binding. Tangential sections of tissue were cut at E14.5 and then incubated with 1 nM AP-Sema3E. Binding was then detected by reaction with an AP substrate. Plexin-D1 (black arrows in A) is highly expressed within the TG (dotted red outline) and the trigeminal nerves that project both centrally toward the brainstem and peripherally towards the snout (right side from dotted green outline). But Plexin-D1 protein is extremely low in nerves when they reach the whisker follicle (white arrowhead in B and C). In contrast, Plexin-D1 protein is strongly detected in the blood vessel ring (white arrows in B and C). Yellow arrowhead (in B and C) indicates non-specific signals in membrane structure of the whisker follicle. (C) To identify the relative location of nerve and blood vessel rings, adjacent sections were immunostained with NF (green) and PECAM (red) and overlaid onto the AP-stained sections. (D–E) Neuropilin-1 protein expression is detected by AP-Sema3A (2 nM) binding in the terminal nerve ring (arrowheads in D-E), which completely overlaps with NF-positive nerve ring on the same sections after AP-staining (E). (F–I) Plexin-D1 protein expression is visualized by immunohistochemistry with anti-Plexin-D1. In the TG nerve terminal surrounding the whisker follicles, Plexin-D1 protein expression is extremely low (arrowheads in F and G). In contrast, Plexin-D1 protein is strongly detected in the blood vessel ring (arrows in H and I). Anti-Plexin-D1 displays non-specific signals in the hair sheath and glassy membrane of the whisker follicle (asterisks in F and H). Scale bar: 1 mm (A), 50 μm (BE, F-I). See also Figure S3.