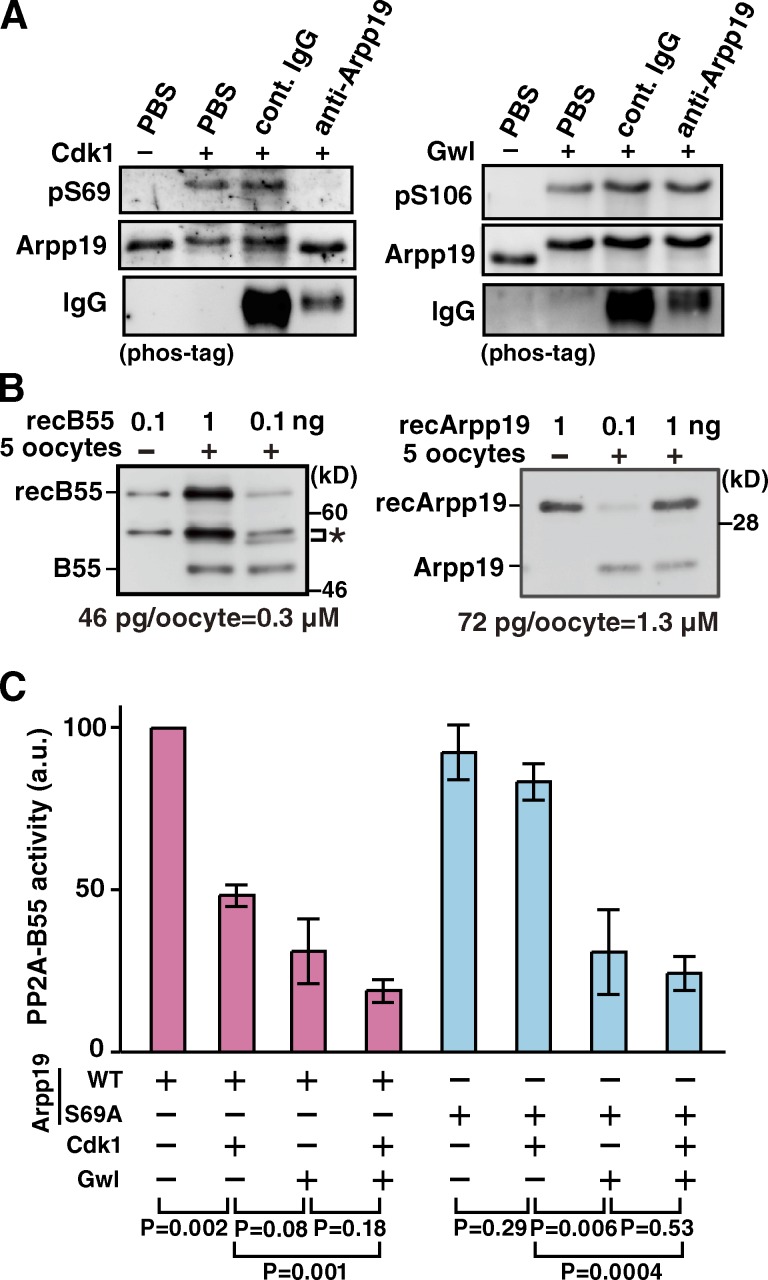
Figure 3.
Ser69 phosphorylation of Arpp19 by cyclin B–Cdk1 converts Arpp19 into an active inhibitor of PP2A-B55. (A) Anti-Arpp19 antibody prevents in vitro phosphorylation on Ser69 of Arpp19 by cyclin B–Cdk1, but not on Ser106 by Gwl. Wild-type Arpp19 was preincubated with anti-Arpp19, control IgG, or PBS, and then phosphorylated with cyclin B–Cdk1 (left) or Gwl (right). Arpp19 phosphorylation was monitored by immunoblot with anti-pSer69 (left) or anti-pSer106 (right). (B) Estimation of the endogenous concentrations of B55 and Arpp19 proteins in starfish oocytes. Indicated amounts of recombinant GST-B55 (recB55; left) or recombinant Arpp19 (recArpp19; right) and/or five starfish oocytes were loaded and analyzed by Western blot. The concentrations of endogenous B55 (left) and Arpp19 (right) were calculated to be 0.3 and 1.3 µM, respectively, from protein amounts of 46 and 72 pg per 3 nl of oocyte volume. Asterisk, nonspecific bands. (C) Arpp19 phosphorylated in vitro on Ser69 by cyclin B–Cdk1 suppresses PP2A-B55 activity. Wild-type Arpp19 or the Ser69Ala (S69A) mutant protein was thiophosphorylated by cyclin B–Cdk1, Gwl, or both kinases, and then mixed with recombinant PP2A-B55 heterotrimers. Final concentrations of PP2A-B55 and Arpp19 in the mixture were adjusted to be 50 and 200 nM, respectively. After removal of kinases, phosphatase activity of PP2A-B55 was measured using Fizzy-pSer50 as a substrate. Each error bar indicates mean value ± SD from three independent experiments.