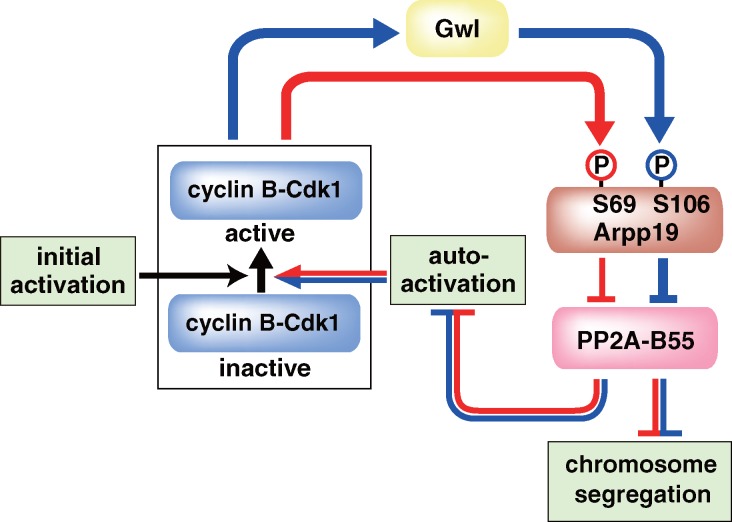
Figure 5.
Model for the two-step phosphorylation of Arpp19 and the distinct roles of the two phosphorylations in governing M phase. First, phosphorylation on Ser69 by cyclin B–Cdk1 (red line) is involved in the autoregulatory activation of cyclin B–Cdk1. Second, further phosphorylation on Ser106 by Gwl (blue line) is needed for proper chromosome segregation, although it is not essential for the autoactivation. Initial activation corresponds to a trigger that reverses the balance between Cdc25 and Myt1/Wee1 before the first activation of cyclin B–Cdk1. Although molecular identity of the trigger remains elusive in most systems, it is clearly identified as Akt/PKB in the starfish oocyte (Okumura et al., 2002; Kishimoto, 2011): 1-MeAde causes activation of Akt/PKB, which in turn directly phosphorylates and inhibits Myt1 and phosphorylates and activates Cdc25, thus tipping the balance toward the initial activation of cyclin B–Cdk1.