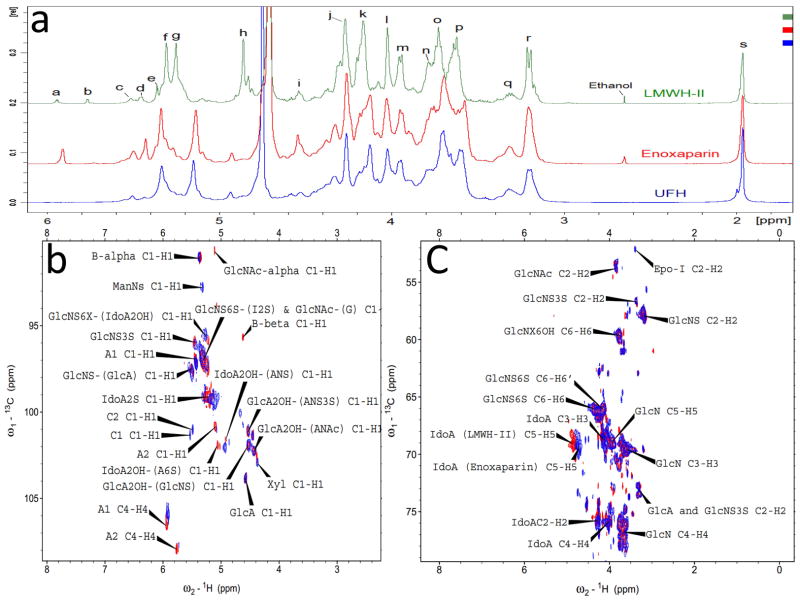
Figure 3.
1D 1H-NMR and 2D HSQC spectra of heparins. Panel a: Comparison and assignments for UFH, enoxaparin and LMWH-II. a, H4 ΔUA2S; b, ΔUA2OH; c, H1 ANS6X-(G); d, H1 ANS3S; e, B molecule of α configuration in panel I and III of Fig. 1; f, H1 ANS6X-(I2S) and ANAc6X-(G); g, H1 I2S; h, H5 I2S; i, H1 G; j, H2 I2S; k, H3 I2S; l, H4 I2S; m, H5 ANS6S; n, H6 ANS; o, H4 ANS6S; p, H3 ANS6X; q, H2 G and A3S,3SNS; r, H2 ANS6X; s, acetyl CH3 (A, glucosamine; I, iduronic acid; G, glucuronic acid). Panel b: Anomeric region comparison and assignments for LMWH-II (red) and enoxaparin (blue). A1 and A2, ΔUA2OH and ΔUA2OH, two types of A molecules in panel I and III of Fig. 1; B-alpha and B-beta, B molecules of α and β configurations in panel I and III of Fig. 1; C1 (Fig. 1 Panel 3) and C2 (Fig. 1 Panel 4), C molecules in Fig. 1 Panel III; Panel c: Aliphatic region comparison and assignments for LMWH-II (red) and enoxaparin (blue). Epo-I, epoxide formed from the alkaline treatment of I2S (Fig. 1 Panel 2). Selected signals were labeled based on the assignments of Guerrini et al25.