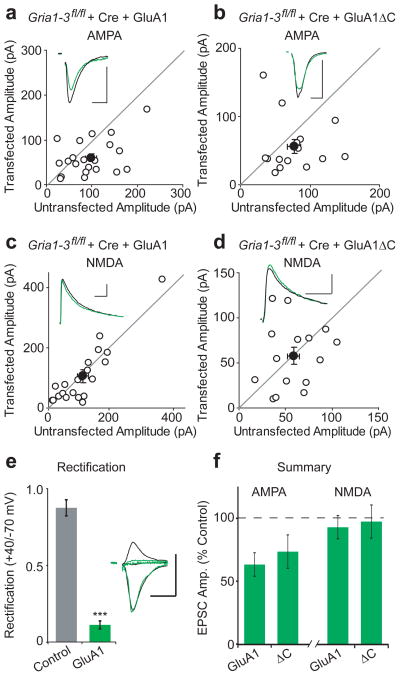
Figure 2. GluA1ΔC has normal synaptic targeting.
Paired whole-cell recordings from control and Cre/GluA1 or Cre/GluA1ΔC-expressing CA1 neurons in Gria1-3fl/fl organotypic slice cultures. (a,c) Full-length GluA1 rescued synaptic AMPAR EPSCs to 68% of control cells (n = 13 p > 0.05), while NMDA EPSCs remained unchanged between control and transfected cells (p > 0.05). (b,d) Replacement with GluA1ΔC results in 73% rescue of AMPA EPSCs without a change in the NMDA EPSC (n = 15, both p > 0.05). (e) Replacement with GluA1 showed inwardly rectifying EPSCs (n = 8, p < 0.01). (f) Summary graph of AMPA and NMDA EPSC rescue between GluA1 and GluA1ΔC. Example traces show average EPSCs for paired control (black) and replacement (green) neurons. Scale bars: 20 msec (AMPA), 100 msec (NMDA), 50 pA. Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m.