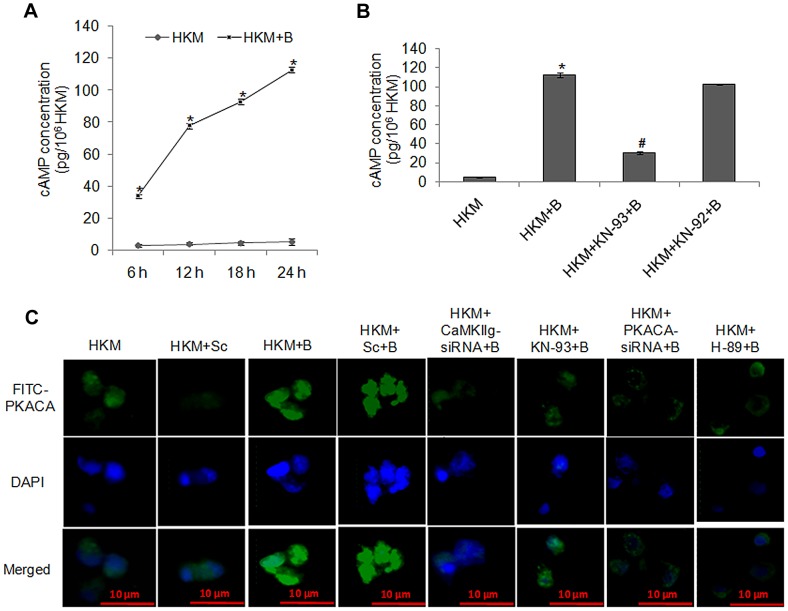
Figure 3. A. hydrophila-infection triggers cAMP release, induces activation and nuclear translocation of PKACA.
(A) Cell lysates of HKM infected with A. hydrophila were checked for intracellular cAMP release at indicated time point p.i. using EIA kit. (B) HKM pre-treated with KN-93 or KN-92 were infected with A. hydrophila and cAMP release was measured in the cell lysates at 24 h p.i. (C) HKM were transfected with CaMKIIg-siRNA, PKACA-siRNA or scrambled siRNA or pre-treated with KN-93 or H-89 then infected with A. hydrophila and PKACA activation and nuclear translocation checked by immunofluorescence. The images are representative of three independent experiments. Vertical bars represent mean ± SE (n = 6). *P<0.05, compared to HKM; #P<0.05, compared to HKM+B. HKM, control head kidney macrophage; HKM+Sc, HKM transfected with scrambled siRNA; HKM+B, HKM infected with A. hydrophila; HKM+Sc+B, HKM transfected with scrambled siRNA infected with A. hydrophila; HKM+CaMKIIg-siRNA+B, HKM transfected with CaMKIIg-siRNA infected with A. hydrophila; HKM+PKACA-siRNA+B, HKM transfected with PKACA-siRNA infected with A. hydrophila; HKM+KN-93+B, HKM pre-treated with KN-93 infected with A. hydrophila; HKM+KN-92+B, HKM pre-treated with KN-92 infected with A. hydrophila; HKM+H-89+B, HKM pre-treated with H-89 infected with A. hydrophila.