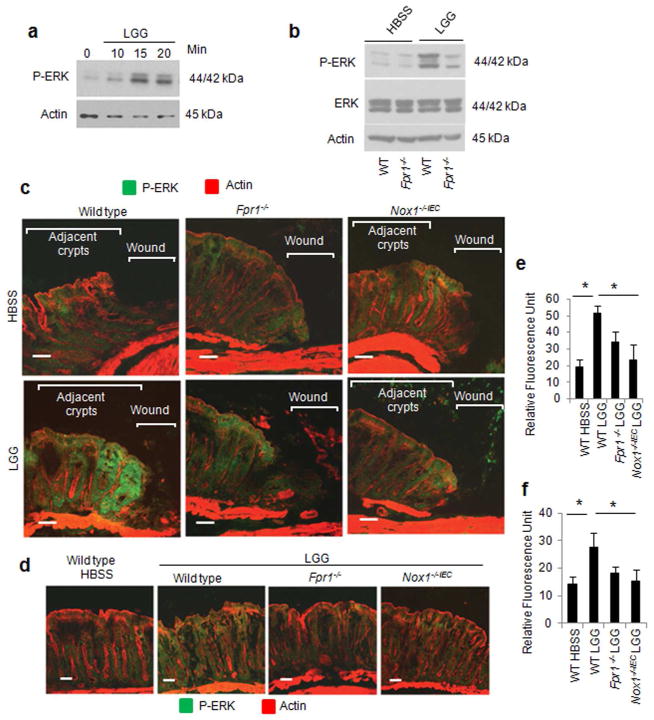
Figure 5.
Commensal bacteria-stimulated ERK activation in crypts adjoining mucosal wounds requires FPR1 and NOX1. (a) Immunoblot analysis for phospho-ERK in colonic epithelial scrapings from harvested biopsy wounds located in the distal colon of wild type and Fpr1−/− mouse after intrarectal administration of HBSS or LGG for 15 min. Data are representative of two independent experiments with n=3 mice per group. (b and c) Immunofluorescence analysis of phospho-ERK in thin sections of colonic tissues from mice treated intrarectally with LGG (2.5×109 cfu) or HBSS for 15 min. (b) Biopsy wounds. n=7 lesions per group. Scale bar, 50μm. (c) Intact colonic mucosa. (d and e) Quantitative representation of immunofluorescence analysis of phospho-ERK in b and c. Results are shown as means ± SD and *P < 0.05 by Student’s t test. Data are representative of three independent experiments with n=3 mice per group.