Figure 3.
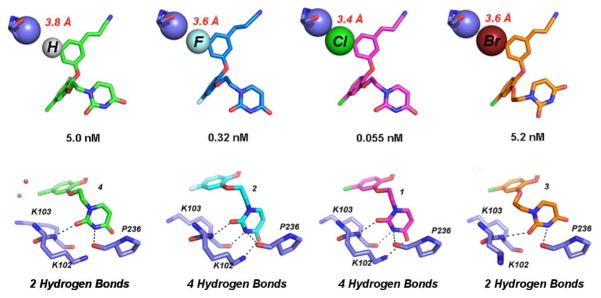
(Top) van der Waals sphere representation of the interaction between the Cγ atom of Pro 95 (lavender) and the C5 substituents of 4, 2, 1, and 3 from Left to Right. The 5-Cl (pink) and 5-F (blue) derivatives maintain the most hydrogen bonds and have potency in the picomolar range, while the interaction with 5-H (green) and 5-Br (orange) are not as strong. The repulsive effect causes the 5-Br to shift away from the Cγ causing a rearrangement of the uracil in order to avoid steric clash. (Bottom) Corresponding uracil conformation for the various C5 derivatives and the possible hydrogen bond interactions (black dashed lines) made with the donors and acceptors in the groove region of the NNBP. Hydrogen bonding potential for the C5 derivatives and strength of the C5-Cγ interaction correlate well with the EC50 values.
