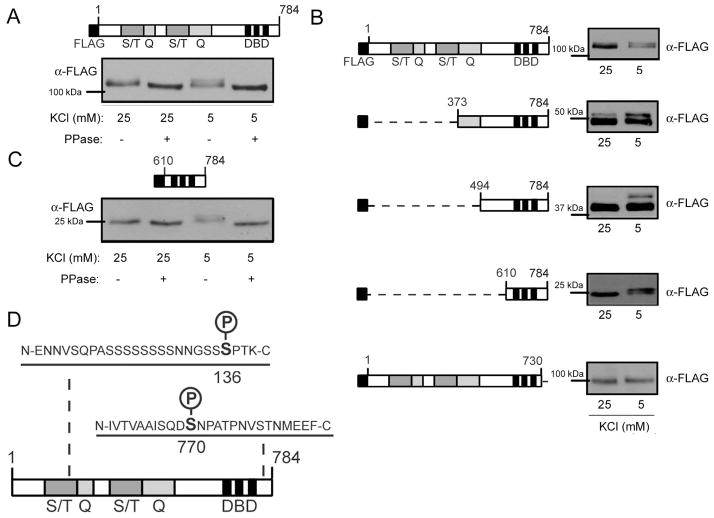
Figure 2. The C-terminal 54 amino acids of Sp4 are required for phosphorylation in resting conditions.
A. Top – Diagram of full-length FLAG-Sp4. Sp4 protein domains are defined as follows: S/T – serine/threonine rich region; Q – glutamine rich region; DBD – DNA binding domain. Bottom – FLAG-Sp4 was transfected into CG neurons and cells were exposed to 25mM (depolarizing) or 5mM (resting) KCl for one hour. Lysates were treated with phosphatase (PPase), separated by 6% PAGE, and analyzed by Western blot. Results are a representative immunoblot. B. Left - Diagram of FLAG-Sp4 deletion mutants transfected into CG neurons and assayed for reduced mobility in resting conditions. Right – A representative immunoblot of each deletion mutant. Lysates were separated by 6% PAGE for 1–784 and 1–730; 8% PAGE for 373–784 and 494–784; and 10% PAGE for 610–784, and the positions of molecular weight markers are indicated. C. Top – Diagram of truncated FLAG-Sp4 610–784. Bottom - Truncated FLAG-Sp4 610–784 was transfected into CG neurons and cells were treated as in (A). Lysates were separated by 10% PAGE and analyzed by Western blot. Results are a representative immunoblot. D. Purified Sp4 from rat cerebellum was analyzed by mass spectrometry, and phospho-peptides were identified corresponding to human S136 and S770.