Figure 1.
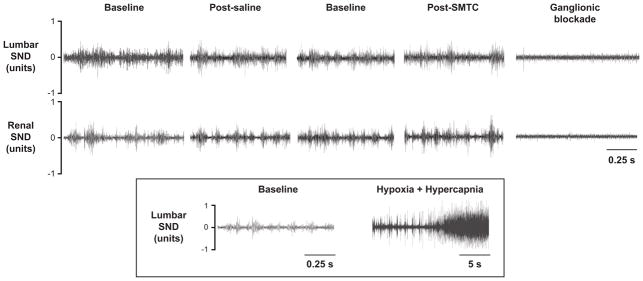
Original tracings of lumbar and renal sympathetic nerve discharge (SND) recordings for the baseline periods, saline and SMTC (0.56 mg/kg) conditions, as well as following ganglionic blockade via chlorisondamine from a representative rat. The inset shows an original lumbar nerve recording in which combined hypoxia and hypercapnia were implemented (following saline and SMTC) to provide a positive physiological control and establish that increased SND, should it occur, can be detected.
