Fig. 4.
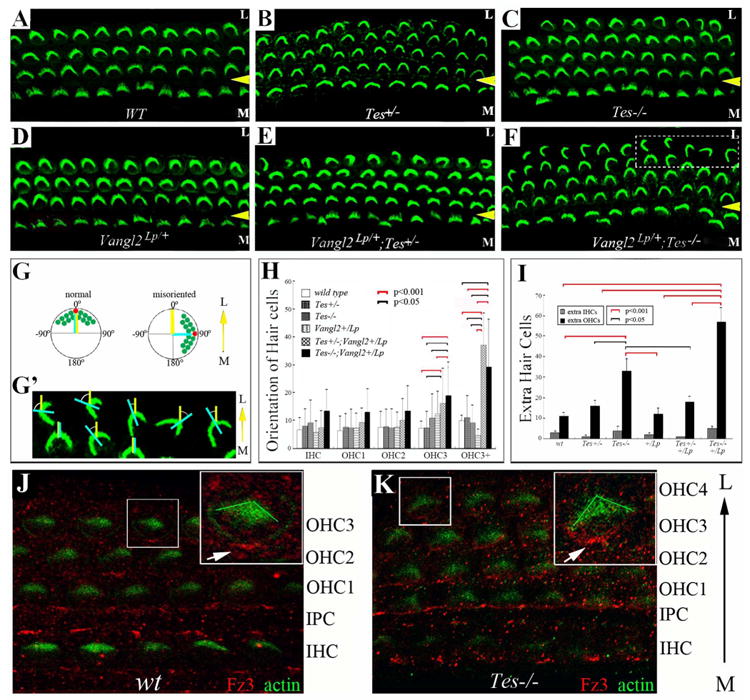
Testin is involved in cellular patterning and hair cell orientation in the cochlea.
(A-F) Cochlear whole mounts were prepared from wild type (WT) (A), Testin+/- (Tes+/-) (B), Testin-/- (Tes-/-) (C), Vangl2Lp/+ (D), Vangl2Lp/+;Tes+/- (E), and Vangl2Lp/+;Tes-/- (F) animals at P6. The samples were stained for phalloidin to visualize actin-rich stereocilia (green) of hair cells. The yellow arrowheads mark the outer pillar cell region that separates the inner (IHCs) from outer hair cells (OHCs). M: medial region of the cochlea duct; L: lateral region of the cochlear duct. The control organ of Corti consists of one row of inner and three rows of outer hair cells (A). Extra rows of outer hair cells were seen in the heterozygous and homozygous Testin mutants (B, C), as well as in Testin and Vangl2 compound mutants (E, F). (G-G′) Schematic diagrams illustrating the measurement of hair cell orientation. The yellow line in (G,G′) represents the medial-to-lateral radius of the cochlear spiral, and the light blue line in (G,G′) is the bisecting line of the V-shaped stereocilia bundle of hair cells. The angle formed between the yellow and light blue lines is the angle measured to represent the orientation of each hair cell. The measurement of the hair bundle orientation is illustrated in (G′) using hair cell images from the boxed area in (F). (H) The orientation of each row of hair cells from comparable mid-apical region of the cochlea was measured, quantified, and plotted. (I) Extra hair cells were counted and plotted for the genotypes included in (A-F). Pairs of groups with p value <0.005 for their difference were indicated by brackets in (H, I). The red and black brackets indicate the p values are less than 0.001 or 0.005, respectively (H,I). (J-K) Fz3 localization in wild type (J) and Testin-/- (Tes-/-) (K) cochleae at P0 was visualized using an antibody against Fz3.
