Fig. 5.
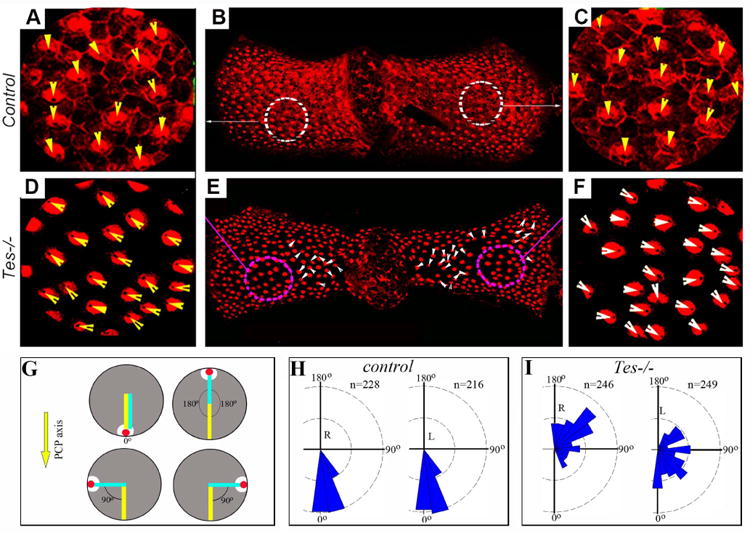
Testin is required for hair cell orientation in the posterior crista.
(A-F) Posterior cristae were prepared from control (A-C) and Testin-/- (Tes-/-) (D-F) animals and stained for an antibody against α-Spectrin. At the apical surface of the vestibular hair cells, the basal body region beneath the kinocilium is devoid of α-Spectrin staining. The arrowheads mark the orientation of hair cells. (G-I) A diagram for hair cell orientation measurement in the posterior crista (G) and plots of hair cell orientation in wild type control (H) and Testin-/- (I) posterior cristae. The red dot and the white area represent the position of the kinocilium and the fonticulus devoid of α-Spectrin staining in a hair cell, respectively (G). The orientation of hair cells from each side of the crista was plotted separately (H, I). 3 cristae for each genotype were used for quantification. R: right side; L: left side.
