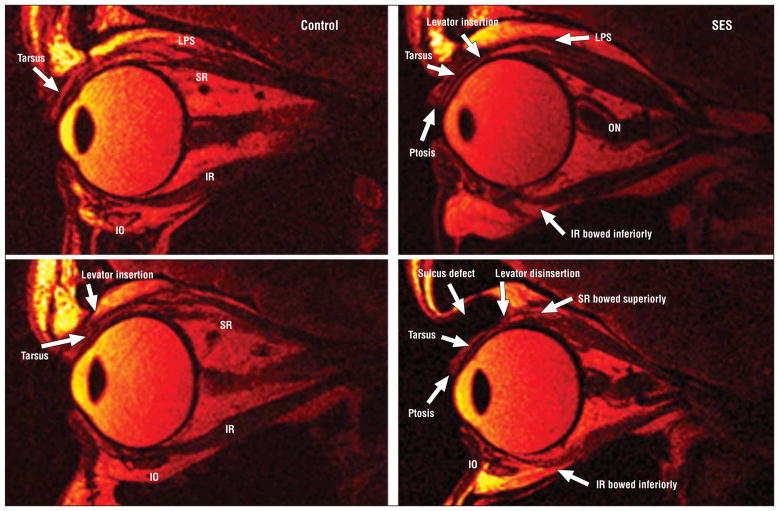
Figure 4.
Fast spin-echo T2-weighted sequence quasi-sagittal magnetic resonance imaging. Left column, Morphology and length of the superior rectus (SR) and inferior rectus (IR) muscles in a young control participant. The insertion of the levator palpebrae superioris (LPS) to the tarsus and normal eyelid anatomy is visible. Top right, Aponeurotic ptosis and bowing of the IR muscle in sagging eye syndrome (SES). The LPS is minimally attached to the tarsus. The optic nerve (ON) is convoluted. Bottom right, Another case of SES showing levator disinsertion, ptosis, and marked superior sulcus defect. The SR and IR are markedly elongated and bowed. IO indicates inferior oblique.