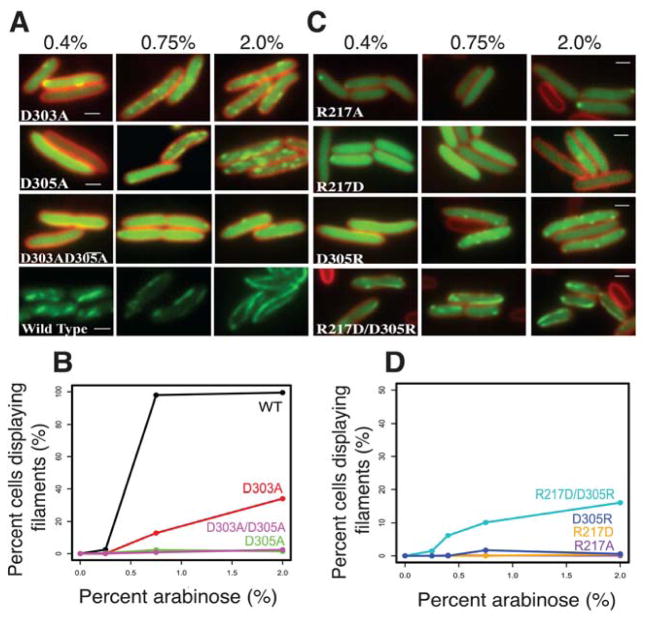
FIGURE 5. PhuZ201 assembles via the same set of lateral surfaces in vivo as in vitro.
(A) and (C) Fluorescent micrographs of uninfected P. chlororaphis cells expressing various GFP-PhuZ201 mutant constructs. (A) Shown are the three tail mutants D303A, D305A and the double mutant D303A/D305A at 0.4%, 0.75%, and 2% arabinose induction. Wild type PhuZ201 is in the last strip for comparison. All mutants have compromised filament formation. (B) Quantitation of data in (A) indicating that of the three mutants, only D303A shows any appreciable polymerization at 2% arabinose. (C) Shown are the four tail mutants R217A, R217D, D305R and the double mutant R217D/ D305R at 0.4%, 0.75% and 2% arabinose induction. The single mutants are unable to make filaments, but the charge reversal in the double mutant partially restores filament formation. (D) Quantitation of the concentration data from (C). All scale bars = 1 micron.