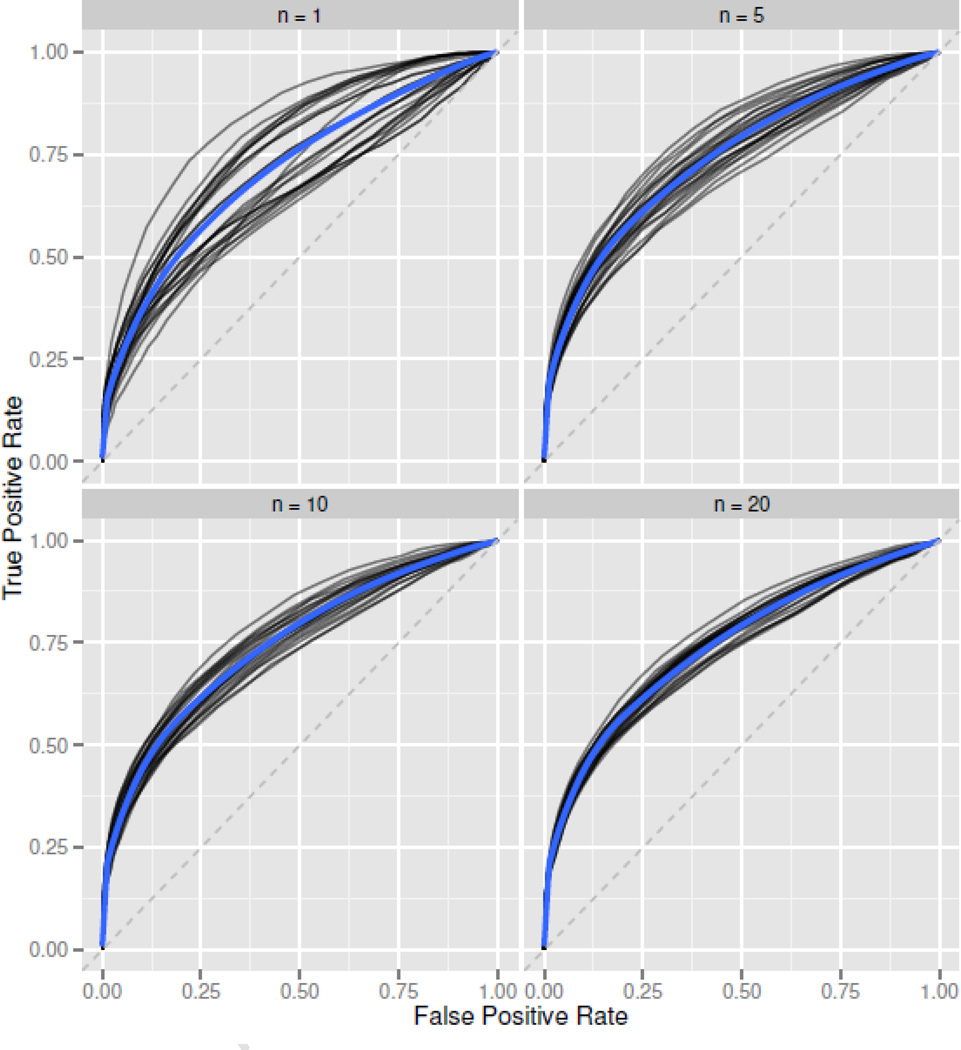
Figure 10. Pooled ROC Variability.
ROCs based on the “Pooled” baseline correction method, using Z-scale normalized peptide intensities in RV144a. Each black line is an ROC generated by randomly sampling n pre-treatment subjects for use as an averaged baseline. The blue line is a smoother applied to the set of black ROCs, giving an “average” ROC for a given sample size. This gives an idea of the variability associated with using a sample size of n as a pooled baseline control. ROC variability decreases quickly as sample sizes increase.