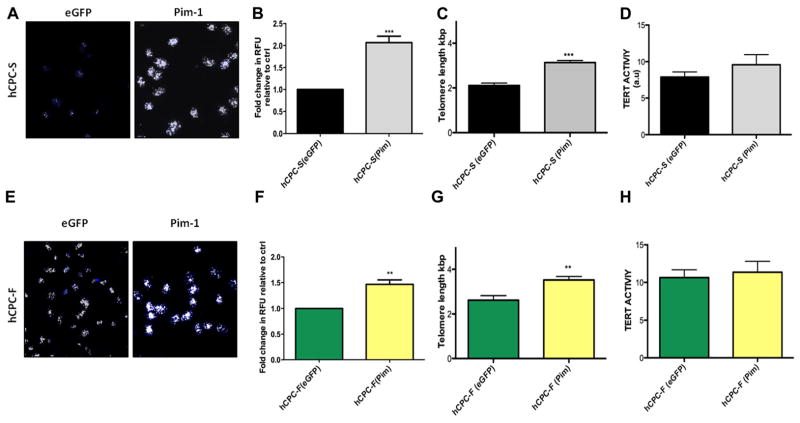
Figure 4. Increased telomere length and telomerase activity after Pim-1 modification.
A and E, Confocal micrographs of telomere staining assessed by quantitative fluorescence in situ hybridization in hCPC with slow-growth kinetics (hCPC-S) and hCPC with fast-growth kinetics (hCPC-F), respectively, white foci indicate telomere staining; blue staining represents nuclei stained with sytox blue (n=3). B and F, Quantitation of telomere length performed by measuring relative fluorescent unit (RFU) by confocal microscope in hCPC-S and hCPC-F relative to their respective enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) controls (n=3; ≈100 cells are included per group). C and G, Increased telomere lengths are observed in hCPC after Pim-1 modification measured by real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis (n=6). D and H, Tert activity measured by TRAPeze assay (n=3) measured in hCPC-S (Pim-1) and hCPC-F (Pim-1) relative to their respective eGFP control hCPC and expressed as arbitrary unit (a.u). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Significance values are calculated for eGFP vs Pim in both hCPC groups.