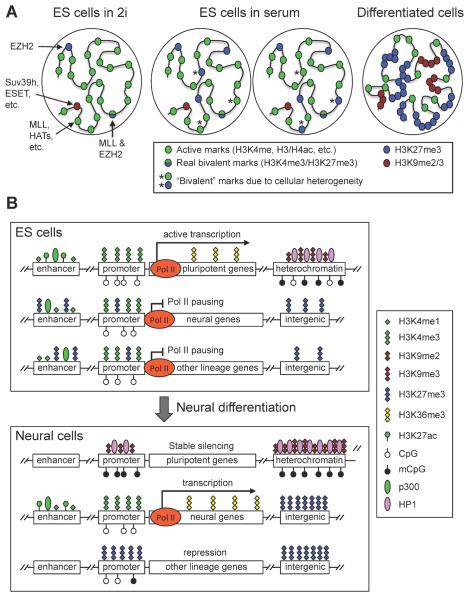
Figure 1. Chromatin states in pluripotent and differentiated cells.
(A) ES cells have a globally `open' chromatin state, characterized by the enrichment of active histone marks such as histone acetylation and H3K4 methylation, whereas differentiated cells have a more compact chromatin state, characterized by expanded domains of repressive histone marks such as H3K27me3, H3K9me2 and H3K9me3. ES cells cultured in 2i medium are highly similar to the naïve pluripotent cells in ICM of blastocysts, and ES cells cultured in serum are more heterogeneous. Some H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 `bivalent' marks may reflect the cellular heterogeneity, especially when ES cells are cultured in serum. (B) Major chromatin features in different genomic regions. In ES cells, the enhancers of both pluripotency-associated genes and developmental genes are enriched with H3K4me1 and p300. The presence of H3K27ac makes enhancers of pluripotency-associated genes active, whereas the lack of H3K27ac and enrichment of H3K27me3 keep enhancers of developmental lineage-commitment genes in a `poised' state. The promoters of pluripotency-associated genes and lineage-commitment genes are also believed to be active and `poised', respectively. Transcriptional elongation is prevented at lineage-commitment genes due to promoter-proximal RNA polymerase II (Pol II) pausing. Upon differentiation toward a specific lineage (e.g. neural lineage), lineage-specific genes acquire active marks at enhancer and promoter regions, and Pol II pausing is released to allow productive elongation. Genes of other lineages lose enhancer marks and gain H3K27me3 at promoters, resulting in repression. Pluripotency-associated genes gain H3K9 methylation and DNA methylation and become stably silenced. During differentiation, heterochromatin regions — characterized by H3K9me2 and H3K9me3, HP1 binding and DNA methylation — are expanded and become more condensed. H3K27me3 in intergenic regions and repressed genes also expands to large domains.