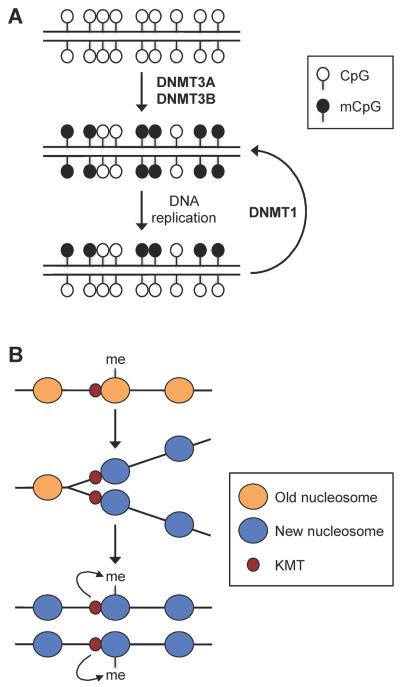
Figure 5. Inheritance of DNA methylation and histone methylation marks through DNA replication.
(A) Semi-conservative maintenance of symmetric CpG methylation. During early embryogenesis, DNA methylation patterns are established by the de novo DNA methyltransferases DNMT3A and DNMT3B. After each round of DNA replication, the maintenance methyltransferase DNMT1 `copies' the CpG methylation patterns from the parental strand onto the daughter strand. (B) Role of lysine methyltransferases (KMTs) in maintaining histone methylation. During DNA replication, methylated histones are replaced by unmodified histones, but KMTs remain associated with newly replicated DNA at specific loci. Following DNA replication, the enzymes methylate the newly incorporated histones to re-establish the methylation patterns.