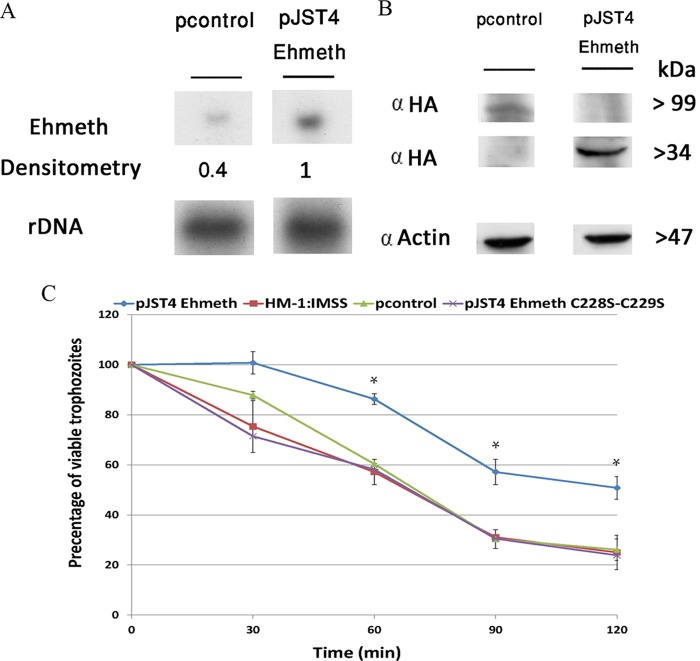
FIG 1.
Overexpression of Ehmeth protects E. histolytica against nitrosative stress. (A) Northern blot analysis was performed using total RNA that was extracted from pJST4-Ehmeth and pcontrol E. histolytica trophozoites. rDNA whose expression was not changed in pJST4-Ehmeth and pcontrol trophozoites were used as controls for RNA loading. The figure displays a representative result from three independent experiments. (B) Western blot analysis was performed on nuclear protein fractions that were prepared from pJST4-Ehmeth and pcontrol E. histolytica trophozoites. The proteins were separated on 12% SDS-PAGE gels and analyzed by Western blotting with an anti-HA (α HA) antibody or an anti-actin antibody. The figure displays a representative result from three independent experiments. (C) The viabilities of wild-type E. histolytica trophozoites from strain HM-1:MSS, E. histolytica trophozoites from a strain that was transfected with a control vector (pcontrol), E. histolytica trophozoites that overexpressed Ehmeth (pJST4-Ehmeth), and E. histolytica trophozoites that overexpressed pJST4-Ehmeth C228S-C229S exposed to 350 μM GSNO for 30, 60, 90, and 120 min were measured. The number of trophozoites at the beginning of each experiment was set at 100%. Bars represent the standard deviations of the means. The means of the different groups for three independent experiments were compared using Student's t test, and statistical significance was set at 5%. The viabilities of the wild-type E. histolytica trophozoites of strain HM-1:MSS, the pcontrol E. histolytica trophozoites, and the pJST4-Ehmeth C228S-C229S E. histolytica trophozoites were not significantly different from each other at any time point, In contrast, the viability of the pJST4-Ehmeth E. histolytica trophozoites was significantly different (P < 0.05) from that of the wild-type E. histolytica trophozoites of strain HM-1:MSS, the pcontrol E. histolytica trophozoites, and the pJST4-Ehmeth C228S-C229S E. histolytica trophozoites after a 60- or 120-min exposure to GSNO.