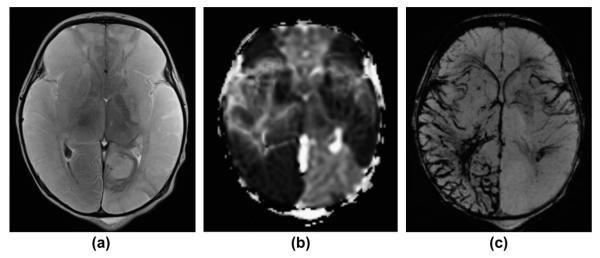
Figure 8.
A 2-day-old term newborn with extensive, multifocal thrombo-embolic strokes (risk factor: chorioamnionitis) with superimposed severe perinatal HIE. (a) Axial, T2-weighted image, (b) apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map, and (c) mIP SWI image show extensive bilateral, T2-hyperintense, ischaemic lesions with matching restricted diffusion (low ADC values) in the territories of the bilateral middle and the right posterior cerebral arteries. In the infarcted areas, mIP SWI shows widened/prominent, marked SWI-hypointense sulcal and intramedullary veins (slow venous flow/partial thrombosis and elevated concentration of deoxygenated haemoglobin). In the regions without restricted diffusion, the sulcal and intramedullary veins are “nearly invisible” (intubated/ventilated neonate). The only exception is the left insular region in which a mismatch between ADC and mIP SWI image is noted. This likely reflects an area with critical residual perfusion.