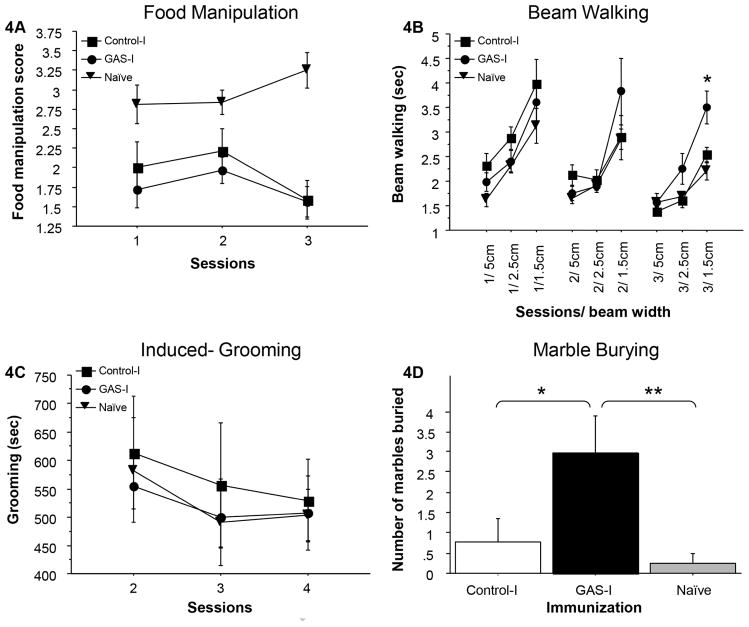
Figure 4.
Effects of passive transfer of IgG from GAS-exposed and control rats to the striatum of naïve rats on (A) food manipulation, (B) beam walking, (C) grooming, and (D) marble burying. (A) The mean and standard error (SE) of food manipulation scores of rats infused with IgG extracted from GAS-exposed rats (GAS-I group, n=8), rats infused with IgG extracted from control rats (Control-I group, n=6) and naïve rats (n=8). (B) The mean and SE of the time spent on the wide and narrow beams of GAS-I rats (n=8), Control-I rats (n=6) and naïve rats (n=8). (C) The mean and SE of the duration of induced-grooming on three sessions of GAS-I rats (n=8), Control-I rats (n=5) and naïve rats (n=8). (d) The mean and SE of the number of marbles buried by GAS-I rats (n=8), control rats (n=5) and naïve rats (n=8).
*p<0.05, **p<0.01