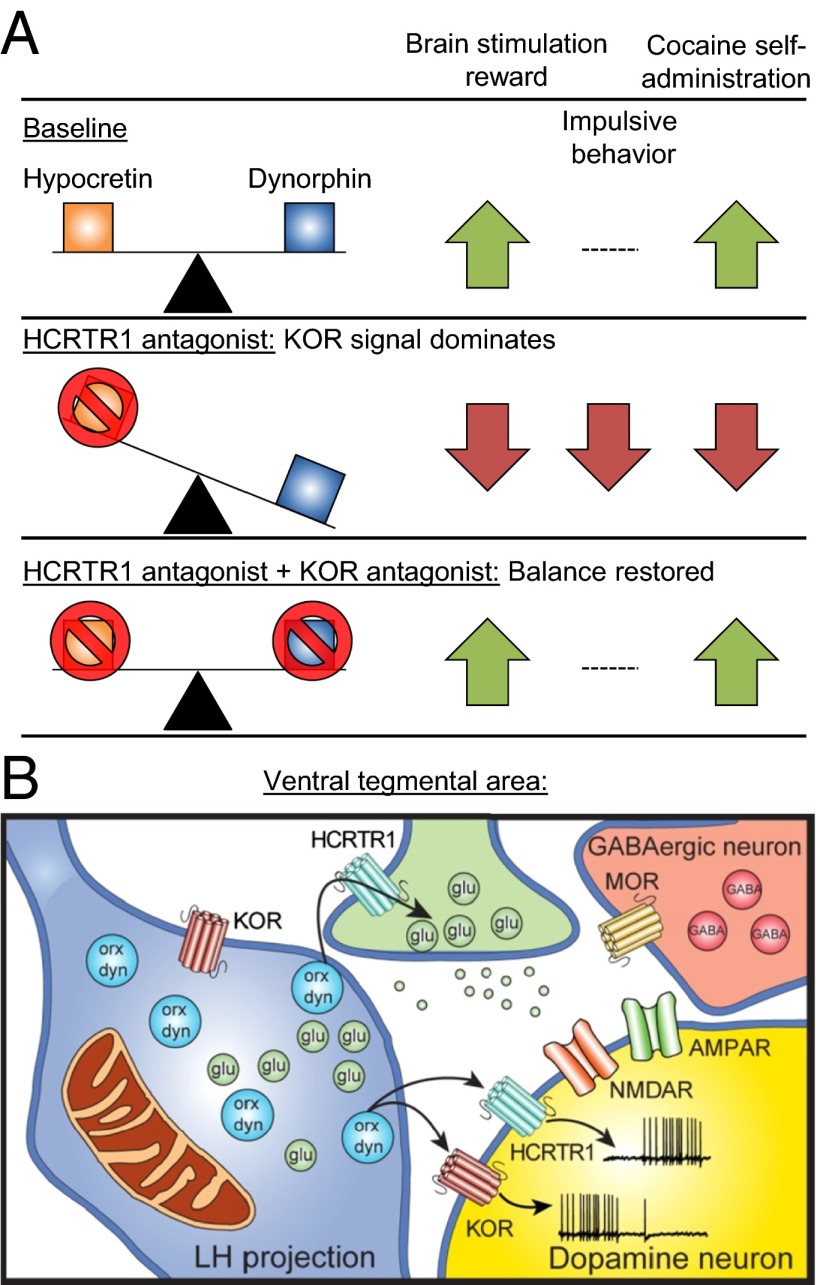
Fig. 1.
(A) Summary of the behavioral findings. Selective blockade of HCRTR1 reveals KOR signaling, which decreases brain stimulation reward, decreases impulsive behavior, and decreases cocaine self-administration. However, concurrent blockade of both HCRTR1 and KOR reverses these effects, returning the behavior in all three tests to the baseline condition. (B) Summary of the electrophysiological findings in the VTA. Lateral hypothalamus (LH) projections to the VTA contain hypocretin and dynorphin in the same vesicles. Dopamine neurons in the VTA express both HCRTR1 and KORs; activation of KORs inhibits and activation of HCRTR1 activates the dopamine cells. Saturation of both receptors produces no net effect on dopamine cells. Hypocretin may act together with excitatory glutamate input to overcome the inhibitory effect of dynophin and GABA transmission onto dopamine cells. dyn, dynorphin; glu, glutamate; MOR, mu-opioid receptor; orx, hypocretin.