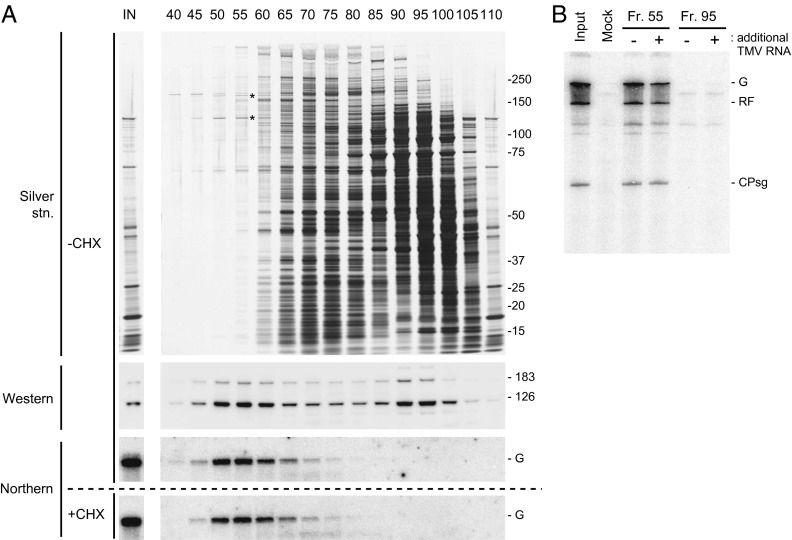
Fig. 1.
Purification of PMTC by SEC. (A) Elution profile. TMV RNA was translated in mdBYL, and the translation mixture was fractionated by SEC using a Sephacryl S-500 column. Protein and RNA from indicated fractions were analyzed by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS/PAGE) followed by silver staining (Top), Western blotting using anti–126-kDa protein antibodies (second panel from Top), and Northern hybridization using a 32P-labeled RNA probe that was complementary to TMV RNA (third panel from Top). (Bottom) The elution profile of TMV RNA for a control sample, in which the translation reaction in mdBYL was inhibited by CHX. Positions of size markers (kDa) are shown on the right, and the 126-kDa and 183-kDa proteins are indicated by asterisks on the silver-stained gel. Positions of the 126-kDa and 183-kDa proteins on the Western blot and TMV genomic RNA (G) on the Northern blots are also indicated. (B) TMV RNA replication tests using fraction nos. 55 and 95. Each fraction was mixed with a P30BYL membrane suspension (for lanes marked with +, purified TMV RNA was also added), incubated at 15 °C for 1 h, and further incubated with [α-32P]CTP and other ribonucleoside triphosphates. RNA was purified, separated using 8 M urea-2.4% PAGE, and 32P signals were detected using an image analyzer (BAS2500). Positions of the genomic (G) and replicative form (RF) RNAs and coat protein subgenomic RNA (CPsg) are indicated on the right.