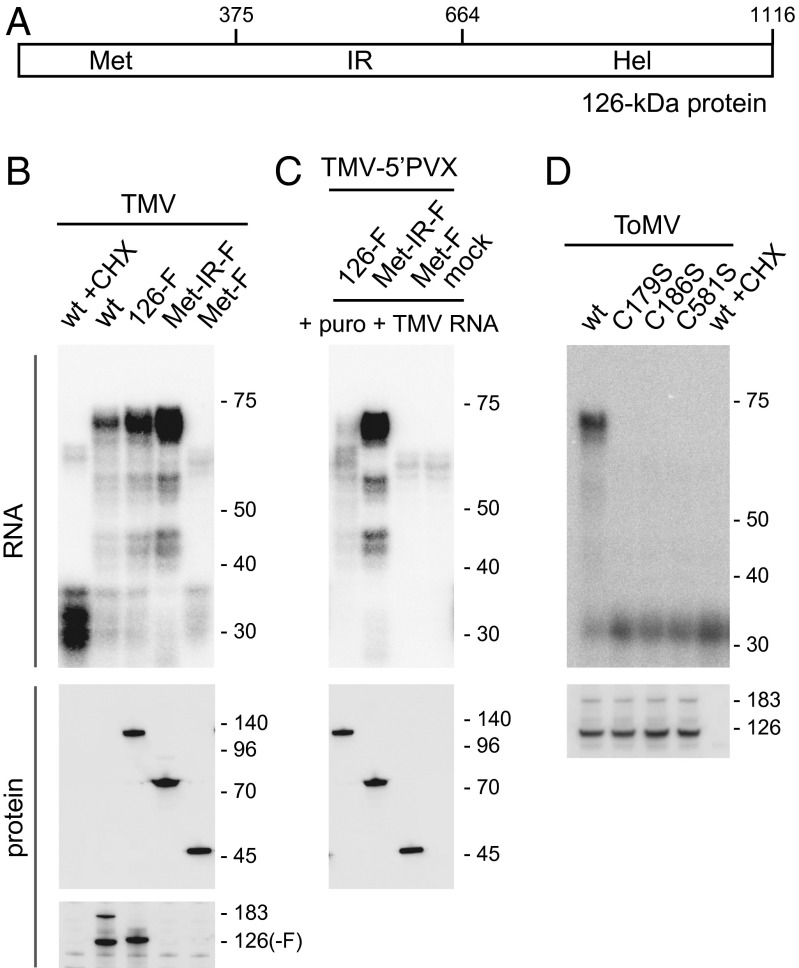
Fig. 6.
Mapping of the region of the TMV 126-kDa protein required for 5′ UTR protection in the PMTC. (A) Schematic diagram of the 126-kDa protein of TMV. Numbers represent amino acid residues from the N terminus. (B) Effect of C-terminal deletions of the 126-kDa protein on the ability to form the PMTC. Indicated TMV derivative RNAs were translated with or without CHX in mdBYL and treated with 1 U/μL MNase. RNA was purified from the reaction mixtures and analyzed as in Fig. 5. The 126-kDa protein and its derivatives were detected by Western blotting using anti-FLAG (Middle) and anti-126-kDa protein (Bottom) antibodies. Positions of RNA size markers (Top, in nt), protein size markers (Middle, in kDa), and the 126-kDa and 183-kDa proteins (Bottom) are indicated on the right. (C) Posttranslational binding of the Met-IR fragment to the 5′ UTR of exogenously added TMV RNA. Indicated TMV-5′ PVX derivative RNAs were translated in mdBYL or mock translated. After translation termination with puromycin, TMV RNA was mixed and incubated, and then treated with 1 U/μL MNase. RNA and protein were analyzed, and the data were presented as in B. (D) Effect of C-to-S mutations of ToMV 126-kDa protein on 5′ UTR binding. Indicated ToMV derivative RNAs were translated with or without CHX in mdBYL and treated with 1 U/μL MNase. RNA was purified from the reaction mixtures and analyzed as in Fig. 3A, except that a 32P-labeled oligonucleotide probe complementary to nucleotides 11–80 of ToMV RNA was used (Upper). Production of the replication proteins was examined by Western blotting using anti-ToMV replication protein antibody (Lower). Positions of RNA size markers (Upper, in nt) and the 126-kDa and 183-kDa proteins (Lower) are indicated on the right.