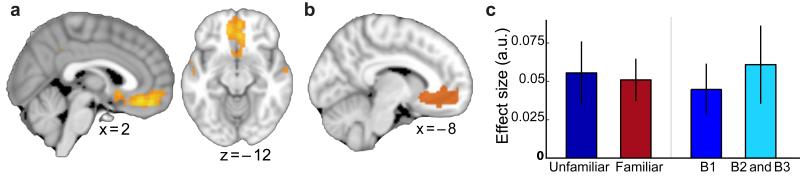
Figure 3. Sensory exposure to a novel good: comparison between the ‘unfamiliar’ and ‘familiar’ groups during the decision making task.
(a) In the familiar group, the mPFC correlated with chosen value during the decision making task (thresholded at p<0.01, uncorrected for visualisation). (b) ROI used to assess value signals in both groups of participants during the decision task. (c) During the decision making task the unfamiliar and familiar groups showed comparable chosen value signals in mPFC (left side: average of all task blocks for each group), and in the unfamiliar group there was no change in the chosen value signal across time (right side: block 1 versus blocks 2 and 3). Parameter estimates were extracted from ROI shown in b (mean ± s.e. across participants).