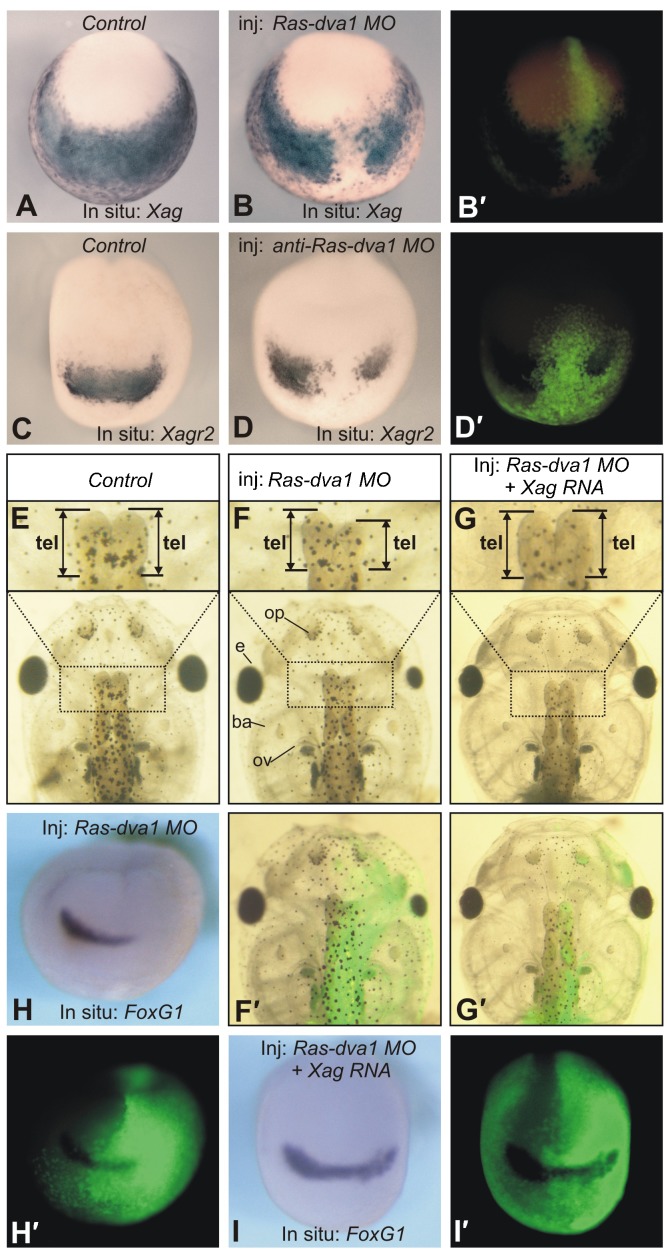
Fig. 3. Inhibition of Ras-dva1 mRNA translation by the Ras-dva1 morpholino elicits the downregulation of Agrs and a reduction of the forebrain.
(A,C) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of midneurula control embryos with dig-labeled probes to Xag and Xagr2, respectively. Anterior view with dorsal side upward. (B,B′,D,D′) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of the Ras-dva1 MO-injected midneurula embryos with dig-labeled probes to Xag and Xagr2, respectively. Fluorescent images in panels B′ and D′ demonstrate distribution of cell clones containing the co-injected FLD fluorescent tracer. (E) The telencephalon (upper row) and whole head of the control 5-day tadpole. Dorsal view, anterior to the top. (F,F′) The telencephalon (upper row) and whole head of the 5-day tadpole developed from the embryos injected with Ras-dva1 MO into the right dorsal blastomere at the 8-cell stage. Note the reduced telencephalon and eye on the injected side. The fluorescent image in panel F demonstrates the distribution of cell clones containing the co-injected FLD fluorescent tracer. (G,G′) Rescue of the Ras-dva1 MO-induced abnormalities by the co-injection of Ras-dva1 mRNA. Note the normal telencephalon and eye on the injected side (see distribution of the injected cells in panel G′). (H,H′) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of the Ras-dva1 MO-injected midneurula embryos with dig-labeled probes to FoxG1. Note the inhibition of FoxG1 expression on the injected side. See the distribution of cell clones containing the co-injected FLD fluorescent tracer in panel H′. (I,I′) Rescue of the Ras-dva1 MO-induced inhibition of FoxG1 expression by the co-injection of Ras-dva1 mRNA. See the distribution of cell clones containing the co-injected FLD fluorescent tracer in panel I′.