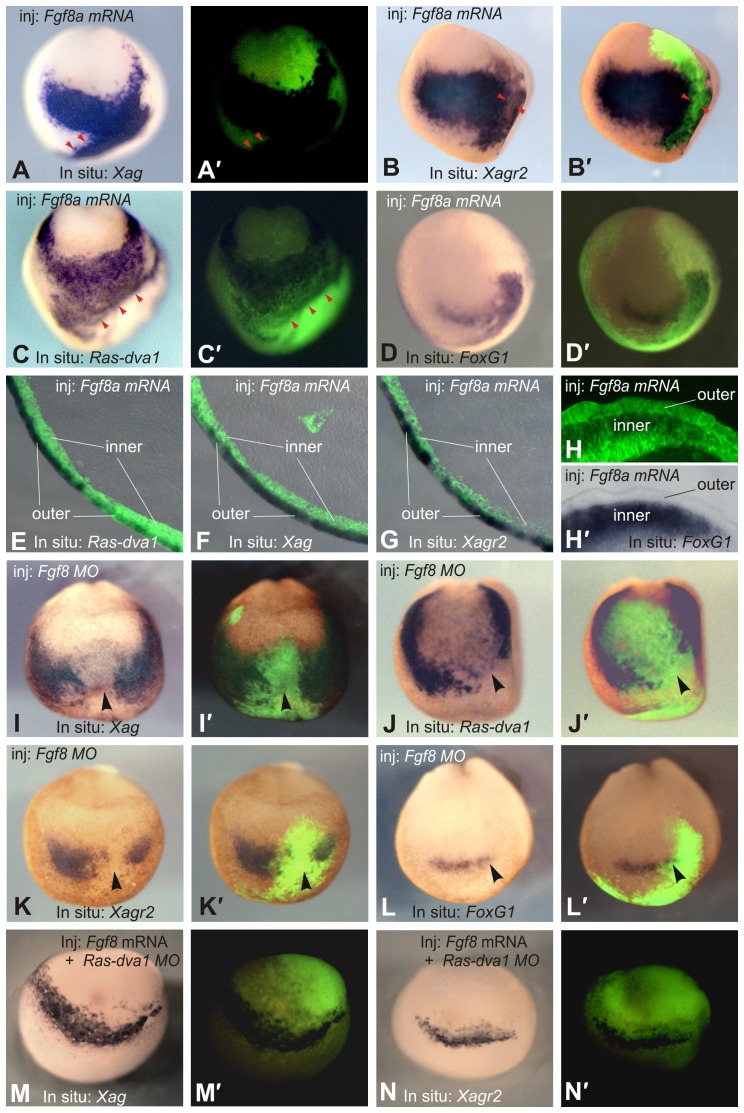
Fig. 4. Fgf8 regulates the expression of FoxG1, Ras-dva1, Xag and Xagr2.
(A–D) Injections of Fgf8a mRNA elicit ectopic expression of FoxG1, Ras-dva1, Xag and Xagr2 in the anterior ectoderm of the midneurula stage embryos. Fgf8a mRNA mixed with FLD tracer was injected at concentration of 20 pg/blastomere in a pair of adjacent animal dorsal and ventral blastomeres on the left sides of 16- to 32-cell stage embryos. Whole-mount in situ hybridization was performed at the midneurula stage. Anterior view with the dorsal side upward. (A′–D′) Overlays of the white light and fluorescent images of embryos shown in panels A–D. Red arrowheads in panels A and C indicate the borders of ectopic expression, which correspond to the borders of cell clones with strong fluorescence. (E–H) Vibratome sections of embryos injected with Fgf8a mRNA. Note that whereas Ras-dva1, Xag and Xagr2 are activated only in the outer layer of the ectoderm (E–G, overlays of bright light and fluorescent images), ectopic FoxG1 is induced exclusively in the inner layer (H,H′). (I–L) Injection of Fgf8a MO leads to inhibition of FoxG1, Ras-dva1, Xag and Xagr2 expression. An Fgf8a MO (1–2 pmol/blastomere) was injected with a FLD tracer in a pair of adjacent animal dorsal and ventral blastomeres on the left sides of 16- to 32-cell stage embryos. (M,N) Co-injection of Fgf8 mRNA is unable to rescue inhibition of Xag and Xagr2 expression elicited by Ras-dva1 MO. The black arrowheads indicate sites of expression inhibition.