Figure 5. sPLA2-IIa stimulates inflammatory cytokine production in conjunctival cells.
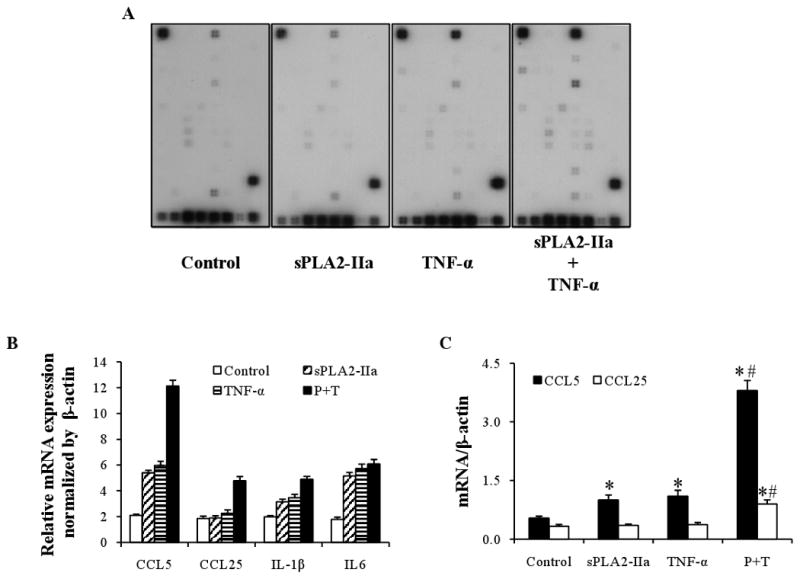
A: Array images. Inflammatory cytokine/chemokine production by human conjunctival epithelial cells was detected by a Pathway-Specific Microarray (SuperArray) assay. The cultures were treated 24 hours with placbo alone as control, sPLA2-IIa (10 μg/ml) or TNF-α (10 ng/ml) alone, or together. After treatments finished, total RNA was isolated and the cRNA was transcriptional labeled with Biotin-16-UTP, hybridized to Oligo GEArray membranes and then conjugated to AP-streptavidin. The signals were developed by addition of a CDP-Star substrate, and image results were detected by scanning.
B: Relative gene expression level of selected genes. Human conjunctival epithelial cells were treated with placebo, sPLA2-IIa alone, TNF-α alone or sPLA2-IIa plus TNF-α for 24 hours. The amount of inflammatory cytokine/chemokine production was then detected. Gene expression profiles were obtained through the analysis using GEAsuite software and the results are presented as mean values of the relative gene expression level.
C: Quantitative real time PCR on CCL5 and CCL25. Human conjunctival epithelial cells were treated with placebo, sPLA2-IIa alone, TNF-α alone or sPLA2-IIa plus TNF-α for 24 hours. cDNA corresponding to 50ng of total RNA was extracted and used for PCR on CCL5 and CCL25. The results are presented as mean values ± SD of two independent experiments with triplicate measurements. *P < 0.05 significantly different from the control. # P < 0.05 significantly different from TNF-α or IL-1β alone.
