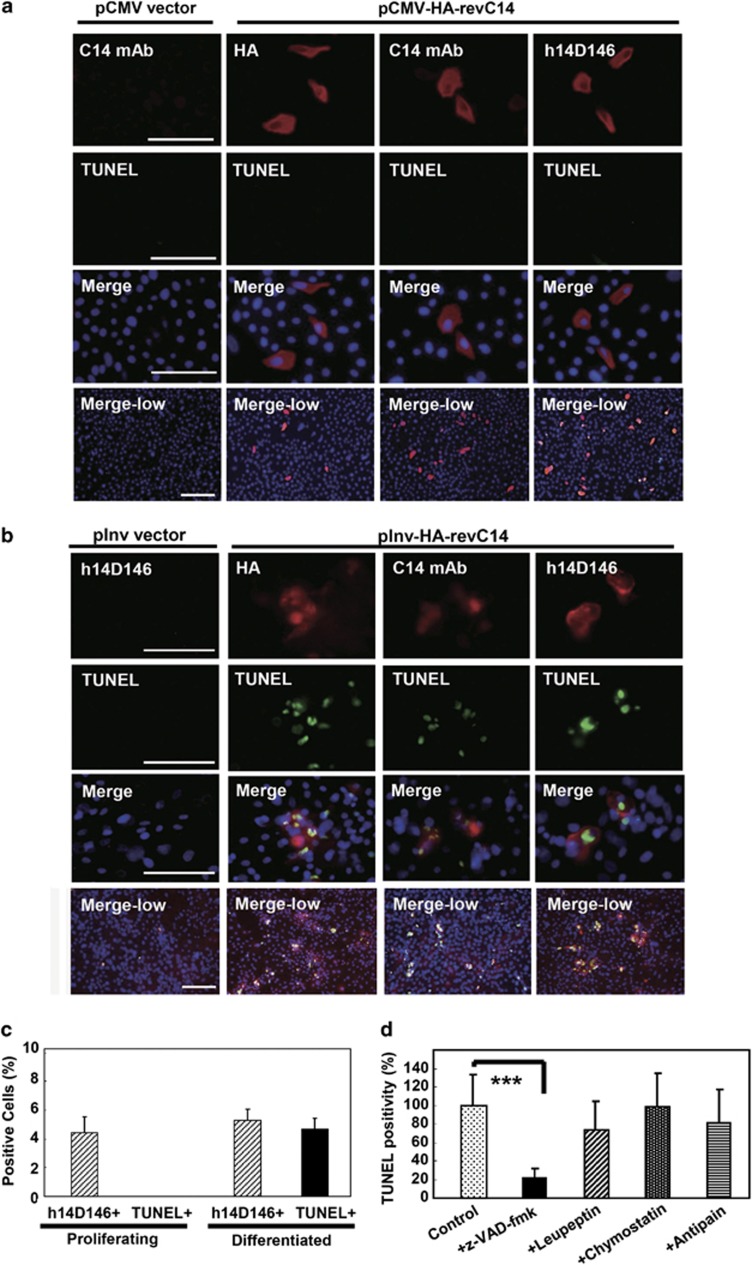
Figure 4.
TUNEL-positive cells emerged among revC14-transfected cells. (a) Immunocytochemical analysis of revC14-transfected cells in the growth phase. Control (pCMV-HA vector only) wells were stained with anti-caspase-14 (C14) mAb. The pCMV-HA-revC14-transfected cells were stained with anti-HA antibody, anti-caspase-14 mAb and anti-h14D146 Ab. The second panel shows TUNEL staining. Merged figures with high magnification (third panel) and merged figures with low magnification (bottom) are shown. Scale bars, 100 μm. (b) Immunocytochemical analysis of revC14-transfected cells in the differentiated phase. Control (pInv-HA vector only) wells were stained with h14D146 Ab. pInv-HA-revC14-transfected cells were stained with the three Abs described above after keratinocyte differentiation. (c) Quantitative analysis of (a) and (b). Approximately 1500–2000 cells were counted for each assay and assays were repeated three times. Each bar indicates the mean±S.D. (n=7). (d) Effects of protease inhibitors on TUNEL positivity. The pInv-HA-revC14-transfected keratinocytes were cultured to confluence. Pan-caspase inhibitor, z-VAD-fmk, leupeptin, chymostatin or antipain was added and incubation was continued in a high calcium condition. After fixation with cold methanol, keratinocytes were stained for h14D146, TUNEL and nuclei (DAPI). TUNEL-positive cells were counted among 1500 cells in 7 fields and the results are summarized in this figure. Significant suppression of TUNEL reaction was found in z-VAD-fmk-treated cells. ***P<0.001