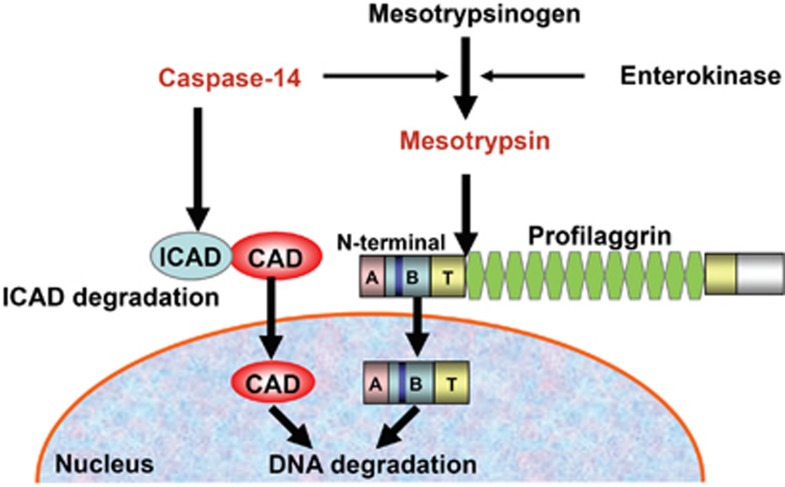
Figure 8.
Involvement of multiple pathways in the denucleation process during keratinocyte terminal differentiation. Two distinct pathways are involved in epidermal denucleation. Activated caspase-14 degrades ICAD and liberated CAD is translocated into the nucleus, resulting in the degradation of chromosomal DNA. On the other hand, activated mesotrypsin cleaves profilaggrin, releasing its N-terminal domain. The free N-terminal domain enters the nucleus and induces DNA degradation. Mesotrypsinogen can be activated by both enterokinase and caspase-14. Thus, these systems appear to work cooperatively, as well as independently, depending on the differentiation conditions