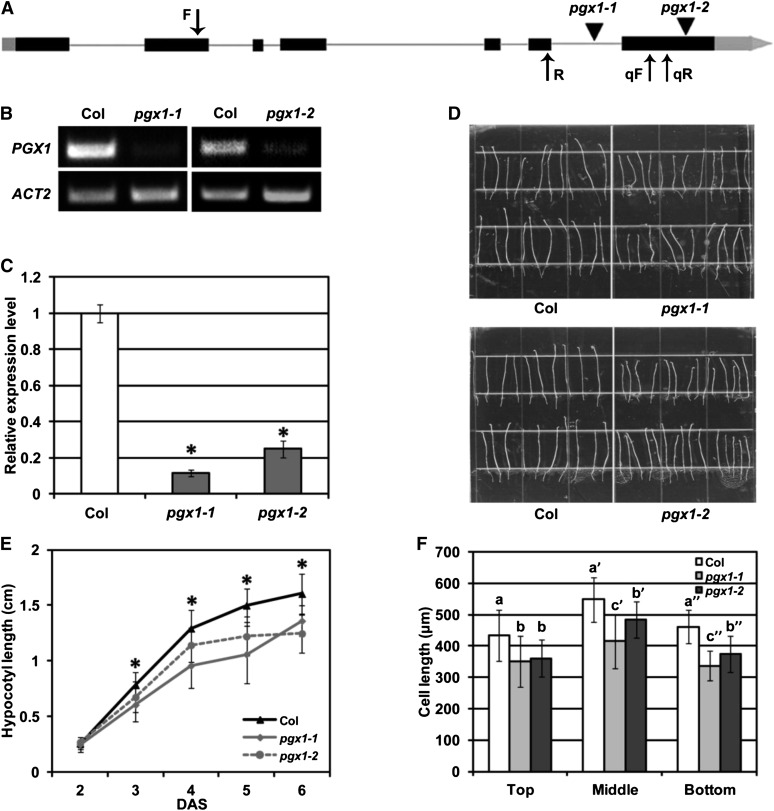
Figure 3.
T-DNA Insertion Mutants of PGX1 Exhibit Reduced Hypocotyl Length.
(A) Schematic gene structure of PGX1 (exons shown as solid boxes, introns as lines, 5′ and 3′ regions as gray boxes, T-DNA insertions as triangles, and primer binding sites as arrows).
(B) and (C) Detection of PGX1 transcript in T-DNA insertion mutants pgx1-1 (WiscDsLox262B06; CS850042) and pgx1-2 (Salk_026818) by RT-PCR (B) and qPCR (C). Error bars indicate sd (n = 6 technical replicates from two independent experiments); ACT2 was amplified as an internal control.
(D) Hypocotyls of 6-d-old etiolated seedlings of Col, pgx1-1, and pgx1-2 mutants grown on MS media without Suc.
(E) Quantification of hypocotyl length for 2- to 6-d-old etiolated seedlings of Col, pgx1-1, and pgx1-2 seedlings (n ≥ 60 seedlings from three independent experiments).
(F) Cell length at the top, middle, and bottom hypocotyls of 6-d-old etiolated Col, pgx1-1, and pgx1-2 seedlings (n ≥ 48 seedlings from two independent experiments). Error bars indicate sd.
Asterisks in (E) indicate significant differences between Col and pgx1 mutant lines (P < 0.001, t test). Lowercase letters in (F) indicate significantly different groups (P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA and Tukey test).