Figure 4.
Specific Mutants of PexRD2 Show Perturbation in Interaction with MAPKKKε and in Oligomerization.
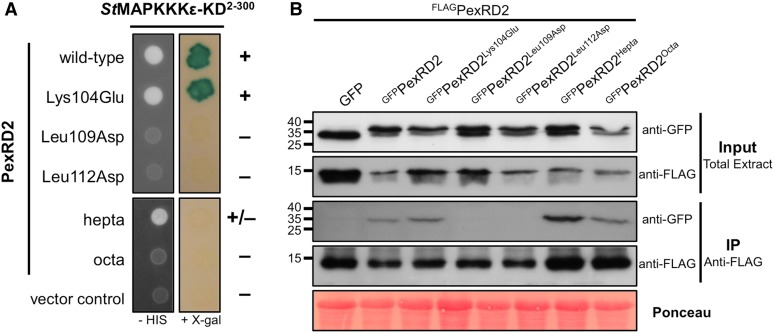
(A) In Y2H, point mutations in two Leu residues within PexRD2’s dimerization interface (Leu109Asp and Leu112Asp), but not the surface presented Lys (Lys104Glu), abolishes the interaction with StMAPKKKε-KD. Point mutations at nine other individual surface exposed residues also had no effect on the interaction (Supplemental Figure 4). Mutation of seven surface presented residues within a variable region of the WY-domain fold (PexRD2hepta) weakens the interaction with StMAPKKKε-KD. The mutation of an additional surface residue (Ala90Glu) within this region (PexRD2octa) leads to a loss of interaction with StMAPKKKε-KD. The symbols + and – denote interaction and absence of interaction, respectively.
(B) In coimmunoprecipitation (IP) from plant tissue, the GFPPexRD2Leu109Asp and GFPPexRD2Leu112Asp variants do not interact with FLAGPexRD2, suggesting they prevent dimerization. All other GFP-tagged variants tested, that targeted surface-presented residues, retain interaction with FLAGPexRD2.