Figure 5.
Mechanistic Description of the Inhibition and Activation Effects on the Rates of Product Formation Using 4-Coumaric Acid as Substrate.
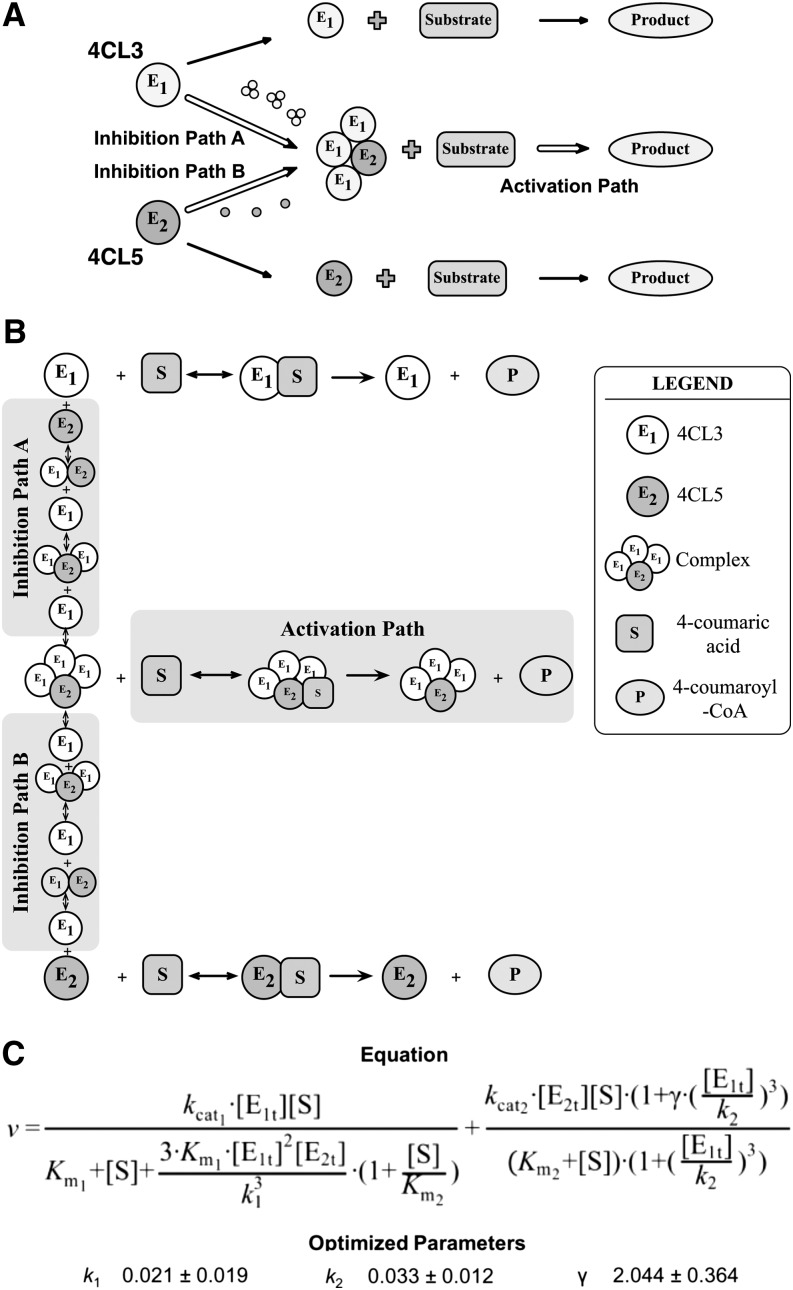
(A) Proposed interactions of 4CL3 and 4CL5 and the effects on product formation. The formation of the 4CL3/4CL5 complex with a 3:1 ratio leads to decreasing amounts of free enzymes and causes a rate reduction (Inhibition Path A and Inhibition Path B). The 4CL3/4CL5 complex is then involved in product formation and results in an increase in rate (Activation Path).
(B) The model described in (A) is extended for one
substrate, 4-coumaric acid, using experimentally derived kinetic parameters,
and deriving rate estimates at each step. Each enzymatic reaction for 4CL3,
4CL5, and the 4CL3/4CL5 complex is based on Michaelis-Menten kinetics.
 and
and 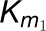 are kinetic parameters of
the 4CL3 enzymatic reaction.
are kinetic parameters of
the 4CL3 enzymatic reaction.  and
and
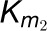 are kinetic parameters of the 4CL5 enzymatic reaction.
are kinetic parameters of the 4CL5 enzymatic reaction.
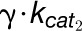 and
and 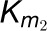 are assumed as kinetic
parameters of 4CL3/4CL5 complex, where
are assumed as kinetic
parameters of 4CL3/4CL5 complex, where 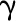 represents activation
effects of the complex on the rate. The interaction rate between 4CL3 and 4CL5
is assumed to be
represents activation
effects of the complex on the rate. The interaction rate between 4CL3 and 4CL5
is assumed to be 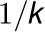 . The interactions occur for the formation of the
4CL3/4CL5 tetramer in succession, which leads to inhibition of the rate.
. The interactions occur for the formation of the
4CL3/4CL5 tetramer in succession, which leads to inhibition of the rate.
(C) A mathematical model is shown for multiple enzymes and
4-coumaric acid as a single substrate. The equation represents the rate of
total product formation associated with 4CL3, 4CL5, and the 4CL3/4CL5 complex,
where [E1t] and [E2t] are the total amounts of 4CL3 and
4CL5 respectively, [S] is the 4-coumaric acid concentration.
k1, k2, and
γ are unknown parameters defined for the
enzyme–enzyme interaction. k1 is
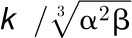 and k2 is
and k2 is
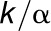 , where
, where 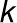 is the
association/disassociation rate between enzyme and enzyme complex in
(A). α and β
are the proportions of 4CL3 and 4CL5 involved with each interaction between
enzymes (see Supplemental Methods for the derivation).
γ represents the product rate of the enzyme complex.
The optimized values of the unknown parameters are fitted by hybrid
optimization using MATLAB. k1,
k2, and γ values
represent the mean ± sd of 100 optimized values.
is the
association/disassociation rate between enzyme and enzyme complex in
(A). α and β
are the proportions of 4CL3 and 4CL5 involved with each interaction between
enzymes (see Supplemental Methods for the derivation).
γ represents the product rate of the enzyme complex.
The optimized values of the unknown parameters are fitted by hybrid
optimization using MATLAB. k1,
k2, and γ values
represent the mean ± sd of 100 optimized values.