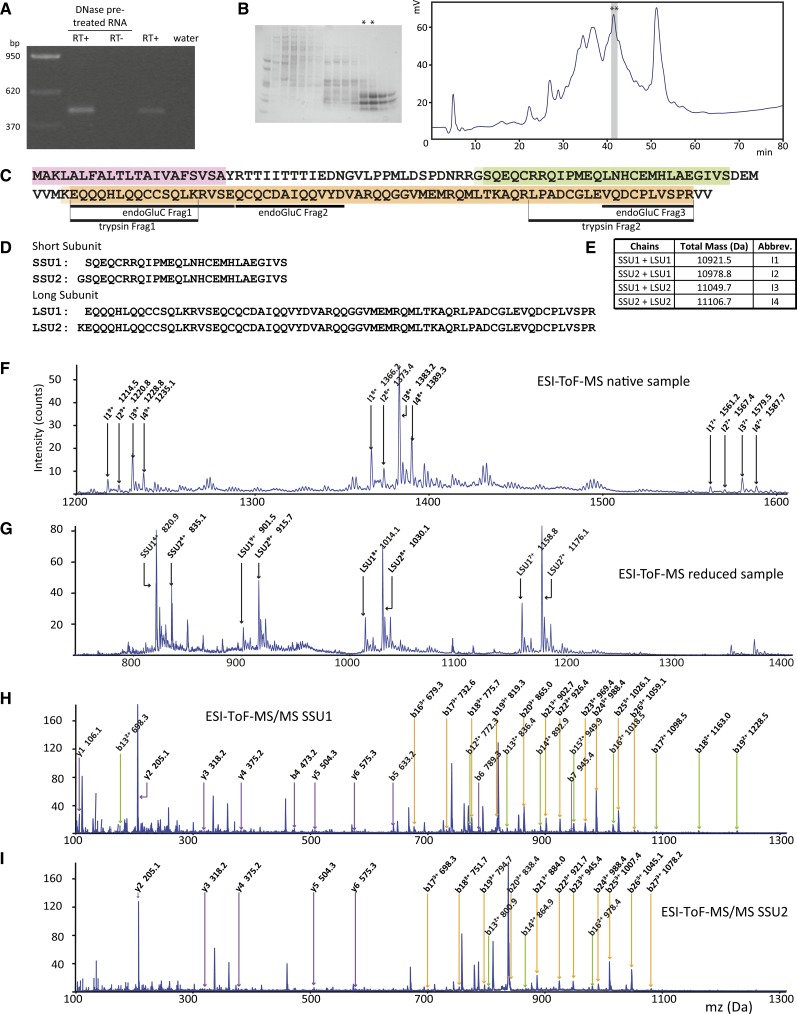
Figure 4.
The Am-PawL1 Gene Is Transcribed, Translated, and Processed into Four Subtly Different Heterodimeric Albumins.
(A) RT-PCR confirmation of Am-PawL1 expression.
(B) Gel image of fast protein liquid chromatography separation of an albumin-rich extract from A. montana seeds. Two fast protein liquid chromatography fractions (asterisks) were further separated by HPLC, and two fractions at 41 min (asterisks) were identified by endo-GluC or trypsin digestion and MS/MS to contain Am-PawL1 mature albumin. For all MS/MS, see Supplemental Tables 10 and 11 for a complete list of ions.
(C) Endo-GluC and tryptic peptide fragments (underlined) mapped onto Am-PawL1. The predicted Am-PawL1 ER signal is highlighted in pink, the mature albumin SSU in green, and the mature albumin LSU in orange.
(D) Am-PawL1 SSU and LSU sequences.
(E) Expected masses for the four SSU/LSU combinations and the abbreviations for each.
(F) ESI-TOF-MS spectrum of the fractions containing native Am-PawL1 albumin. Ions corresponding to the expected masses for each conformation are indicated.
(G) ESI-TOF-MS spectrum of the reduced and alkylated fraction containing the Am-PawL1 albumin.
(H) ESI-TOF-MS/MS spectrum of the peak corresponding to SSU1 (820.9 D). 1+ (purple), 2+ (green), and 3+ (orange) b and y ions are indicated.
(I) ESI-TOF-MS/MS spectrum of the peak corresponding to SSU2 (835.1 D).