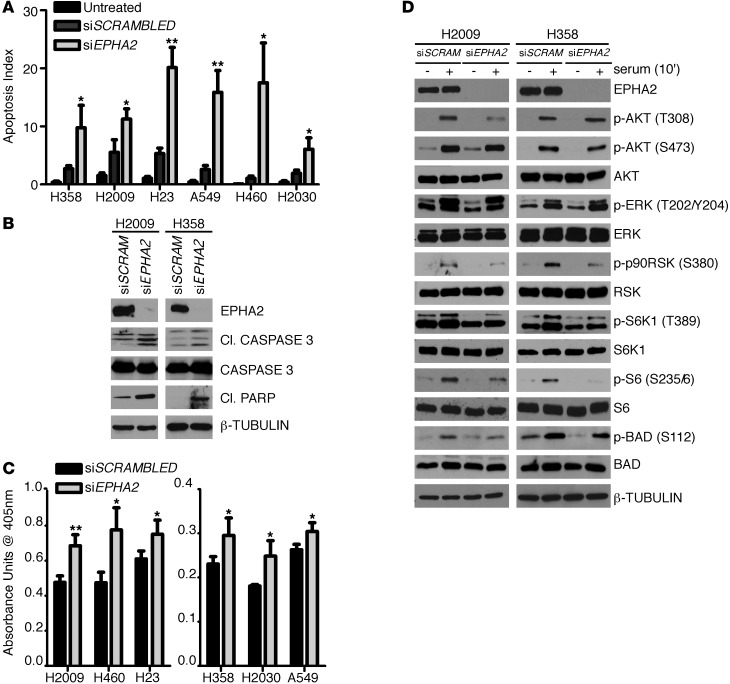
Figure 4. EPHA2 knockdown leads to an increase in apoptosis in NSCLC cell lines.
(A) Cells were treated with scrambled or EPHA2-specific siRNA for 72 hours. Apoptosis was detected via the ApopTag TUNEL assay. Graph represents 3 independent experiments, and data are presented as the percentage of TUNEL-positive nuclei of total nuclei ± SEM. (B) Western blotting of H2009 and H358 cells treated with scrambled or siEPHA2 for 72 hours with 5 μg/ml TRAIL added during the final 24 hours after transfection. Cl., cleaved (caspase-3 or PARP). (C) Apoptosis was measured by quantifying histone-associated DNA fragments using a Cell Death ELISA Kit. Cells were treated with scrambled or siEPHA2 for 72 hours before the assay. All 6 cell lines exhibited a statistically significant increase in apoptosis in the cells treated with siEPHA2 compared with the scrambled controls. Experiments were repeated 3 times, and data are presented as average absorbance unit (AU) ± SEM. (D) H2009 and H358 cells were treated with scrambled or siEPHA2 for 72 hours. Cells were starved for 24 hours and stimulated with 10% serum for 10 minutes before lysis. Shown are representative immunoblots in which phosphorylation levels of signaling molecules were detected using anti-phospho antibodies and EPHA2 expression was detected by an anti-EPHA2 antibody. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.