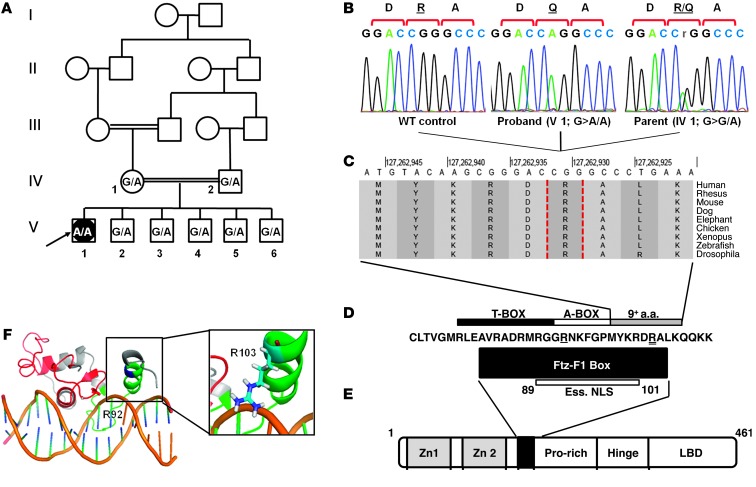
Figure 2. Characterization of the SF1 mutation in the patient’s family.
(A) Pedigree of the patient’s consanguineous family. The proband (V1, arrow) a 46,XY female, has healthy first-cousin parents (IV1 and IV2) and 5 siblings (V2–V6). SF1 c.308 genotype (G, WT; A, mutant) is shown for each. (B) DNA sequencing chromatograms of the c.308G>A mutation (p.R103Q): homozygous in the proband, heterozygous in the mother, absent in a control (subject numbering as in A). (C) Cross-species conservation of the residues adjacent to R103 (dashed vertical outlines). Data were obtained from the UCSC human genome browser (24). (D) Conserved sequence of the Ftz-F1 box, the T-box and A-box subdomains, and the essential nuclear localization signal (Ess. NLS) of SF1 (6, 25). Residues mutated in the R92Q and R103Q mutations are denoted by single and double underline, respectively. (E) SF1 protein domains, including 2 zinc finger motifs, Ftz-F1 box (black box), proline-rich domain, hinge domain, and ligand-binding domain (LBD). (F) 3D model (generated using PyMol software; ref. 26) based on the solution structure of SF1 (7), showing the DNA-binding domain bound to its target sequence in the inhibin α subunit promoter. The 2 zinc finger motifs are shown in red, Ftz-F1 box is green, and R103 is blue. Inset shows the orientation of the R103 side chain, with the positive charge adjacent to the negatively charged DNA backbone.