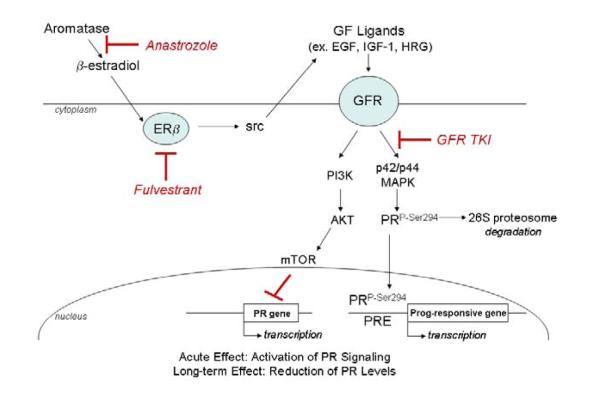
Figure 2. Proposed Model of Ligand-Independent PR Signaling in Lung Cancer.
Growth Factor (GF) ligands will induce Growth Factor Receptor (GFR) signaling, resulting in phosphorylation of PR at ser294 by the MAPK pathway, leading to both ligand-independent receptor activation and induction of proteosome-mediated PR degradation, and/or may lead to direct suppression of PR transcription by the Akt/mTor pathway (with a resultant decrease in PR protein expression). Such a pathway might explain why low PR in lung tumors was associated with worse survival, because it is indicative of high levels of GFR siginaling.