FIGURE 3.
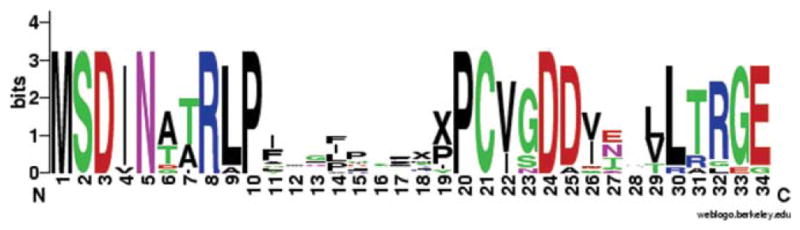
WebLogo alignment of 15 members of the “MSDIN” family (named for the first five highly conserved amino acids). The height of the amino acid at each position represents its degree of conservation. The MSDIN family encodes the amatoxins and phallotoxins and is also predicted to encode a variety of unknown peptides within the hypervariable central region (amino acids 11–20), which is 6–10 amino acids in length (Xs have been inserted in the hypervariable regions of less than 10 amino acids to emphasize the conservation of the carboxy terminus of the MSDIN peptides). As defined here, the “hypervariable” region includes the carboxy-terminal Pro, which is completely conserved in the MSDIN family as well as being a constituent of the mature toxins. Based on cDNA sequences, the M (Met) of MSDIN is the translational start codon. Amino acids 35–39 are not shown, because there is an intron (experimentally established for AMA1 and PHA1; deduced for the others) that interrupts the third to the last codon (Originally published in Luo et al. J Biol Chem 2009, 284, 18070–18077. © the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.).
