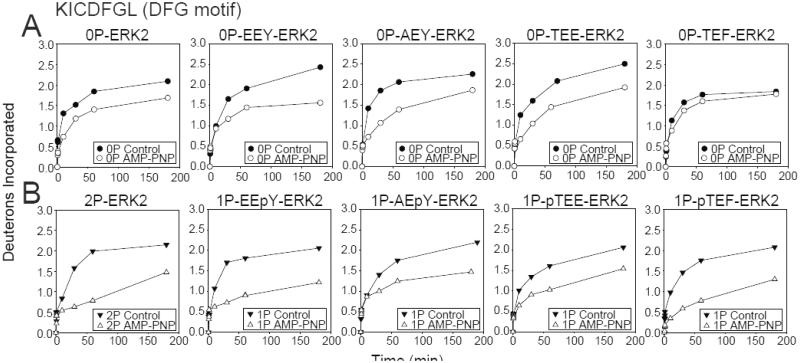
Fig. 4. Monophosphorylation of ERK2 allows domain closure.
Time courses for WT and activation loop mutants, EEY-, AEY-, TEF- and TEE-ERK2, in (A) unphosphorylated and (B) monophosphorylated states. EEpY- and pTEF-ERK2 show significant HX protection by AMP-PNP in the DFG motif to a level comparable with 2P-ERK2, consistent with the active state nucleotide binding mode and domain movement. In contrast, AEpY- and pTEE-ERK2 more closely resemble 0P-ERK2, consistent with the inactive state nucleotide binding mode. Only EEpY-ERK2 enhanced HX within the hinge region, consistent with increased hinge flexibility (see Fig. S4).